Overview
Core exercises for seniors are crucial for enhancing stability, balance, and overall mobility, which significantly reduces the risk of falls and related injuries. The article emphasizes that exercises such as seated leg lifts, standing side leg raises, and chair yoga not only strengthen core muscles but also improve seniors' quality of life by promoting independence and preventing accidents, as supported by various studies and guidelines on safe exercise practices.
Introduction
Seniors today face unique challenges that can significantly impact their quality of life, but there is a powerful solution that lies within their reach: core strength. As the foundation of stability and mobility, a strong core is essential for older adults to maintain balance, prevent falls, and enhance overall well-being.
With alarming statistics revealing that falls are the leading cause of injury among seniors, prioritizing core exercises becomes not just beneficial, but vital. This article delves into the importance of core strength for seniors, offering practical exercises, safety guidelines, and strategies to seamlessly incorporate these movements into daily routines.
By empowering seniors to embrace these practices, HR Benefits Managers can play a crucial role in fostering healthier, safer lifestyles for older adults, ultimately enhancing their independence and quality of life.
Understanding Core Strength: A Vital Component for Seniors
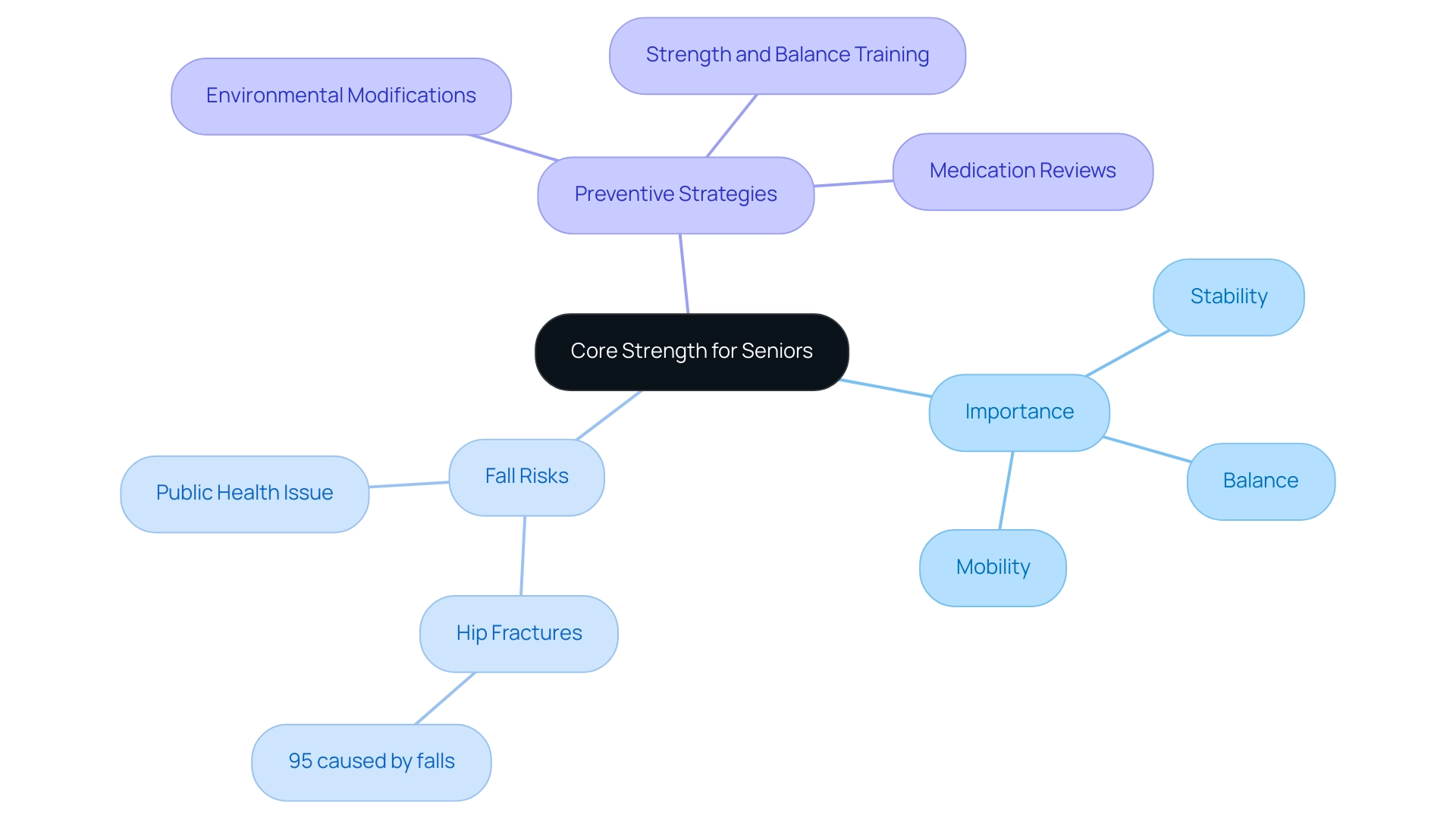
Core strength encompasses the stability and power of the muscles in the abdomen, lower back, hips, and pelvis. For seniors, cultivating strong core muscles is essential for supporting balance, stability, and overall mobility. As individuals age, the risk of falls and related injuries escalates alarmingly—more than 95% of hip fractures in the elderly are caused by falls.
Participating in activities that enhance fundamental strength can significantly reduce this risk. Research has consistently shown that having a strong core enhances balance and coordination, allowing seniors to preserve their independence and improve their quality of life. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) underscores the importance of addressing fall-related issues, noting that sixty-seven percent of fall-related costs are borne by Medicare.
This emphasizes the urgent requirement for effective strategies to avert accidents. The case study titled 'Preventive Strategies for Accidents' illustrates that preventing accidents is more effective than treating injuries, emphasizing the importance of:
- Environmental modifications
- Strength and balance training
- Medication reviews
By prioritizing fundamental strength exercises, HR Benefits Managers can empower their teams to embrace practices that are core for seniors and lead to healthier, safer lifestyles for older adults.
Moreover, the CDC offers various resources for accident prevention, providing valuable information to support these initiatives.
Effective Core Exercises for Seniors: Building Strength Safely
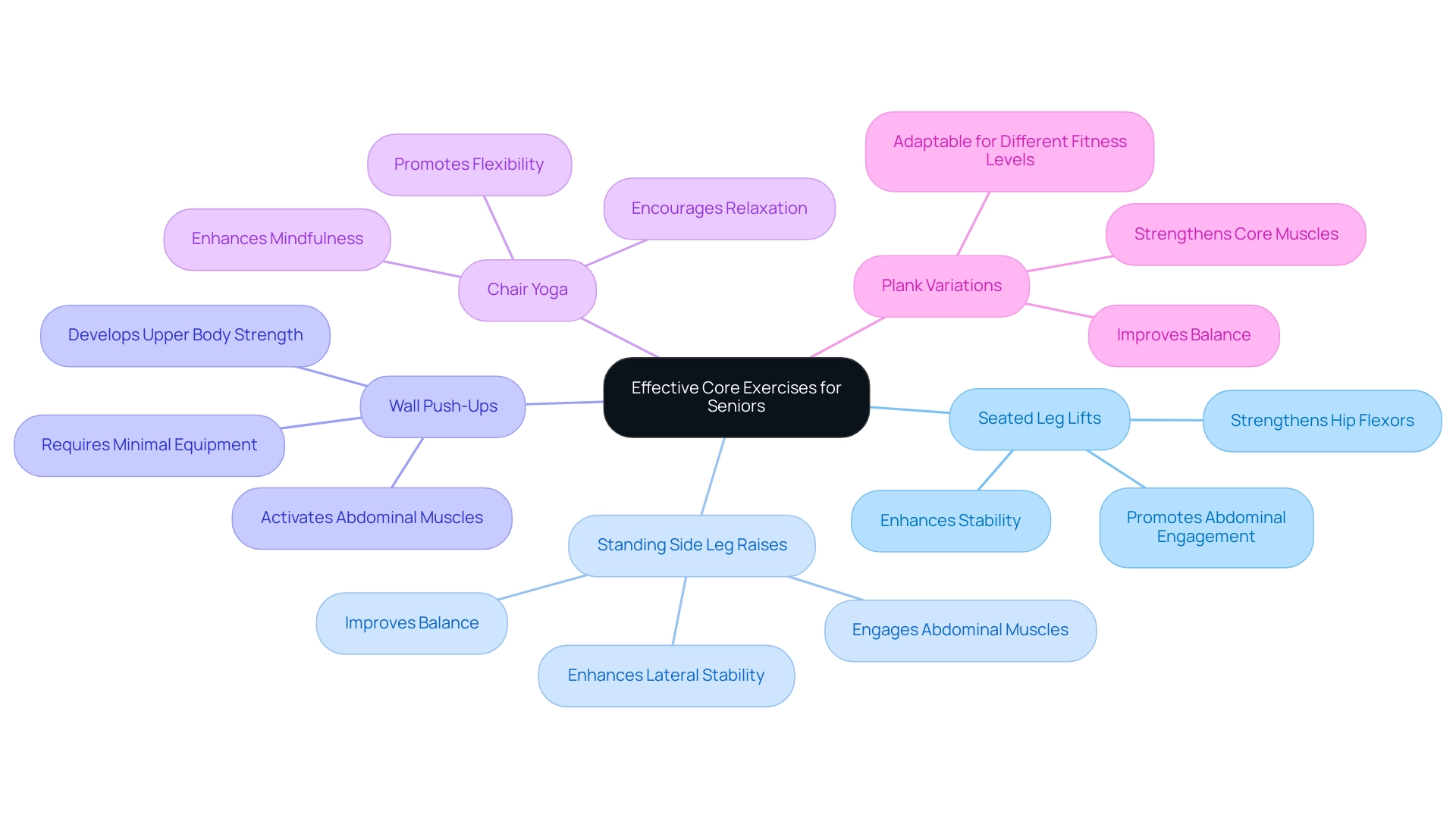
Enabling older adults to enhance their core for seniors is an essential measure in advancing their overall wellness and safety. Research by McGill & Marshall (2012) demonstrates that focused strength activities can significantly enhance stability, which is essential for preventing falls in this demographic. Here are some effective fundamental workouts designed for seniors:
- Seated Leg Lifts: This simple yet effective activity involves sitting comfortably in a chair and lifting one leg at a time, holding it for a few seconds. It mainly enhances the hip flexors and abdominal muscles, promoting stability, which is crucial for lowering fall risk.
- Standing Side Leg Raises: An excellent way to enhance lateral stability, this activity requires seniors to hold onto a chair for support while lifting one leg to the side. Engaging the center during this movement is essential for balance, which aligns with findings from recent case studies that emphasize the importance of abdominal strength in preventing injuries.
- Wall Push-Ups: This exercise is ideal for developing upper body strength while activating the abdominal muscles. By standing at arm's length from a wall and performing push-ups against it, older adults can strengthen their muscles without the need for extensive equipment, promoting overall physical condition.
- Chair Yoga: Yoga poses can be easily adapted for seated positions, promoting flexibility and abdominal engagement. This gentle approach encourages relaxation and mindfulness while working on strength, which is beneficial for injury prevention.
- Plank Variations: Adapted planks executed on the knees enable older adults to concentrate on preserving a straight alignment from head to knees, effectively enhancing abdominal strength without undue strain. This activity also aids in enhanced balance, as emphasized in the case study regarding the effects of physical activity on aging and injury prevention.
Incorporating these routines into a daily regimen can greatly enhance strength and safety. As emphasized in recent studies, activities designed for older adults not only focus on core for seniors but also contribute significantly to preventing falls and injuries. Remember, as fitness expert Boehm emphasizes,
Movements should be slow and controlled; don't throw your arm and leg out as fast as you can.
By prioritizing these safe and effective exercises, you can encourage older adults to take charge of their health and well-being.
The Benefits of Core Training: Enhancing Balance and Stability
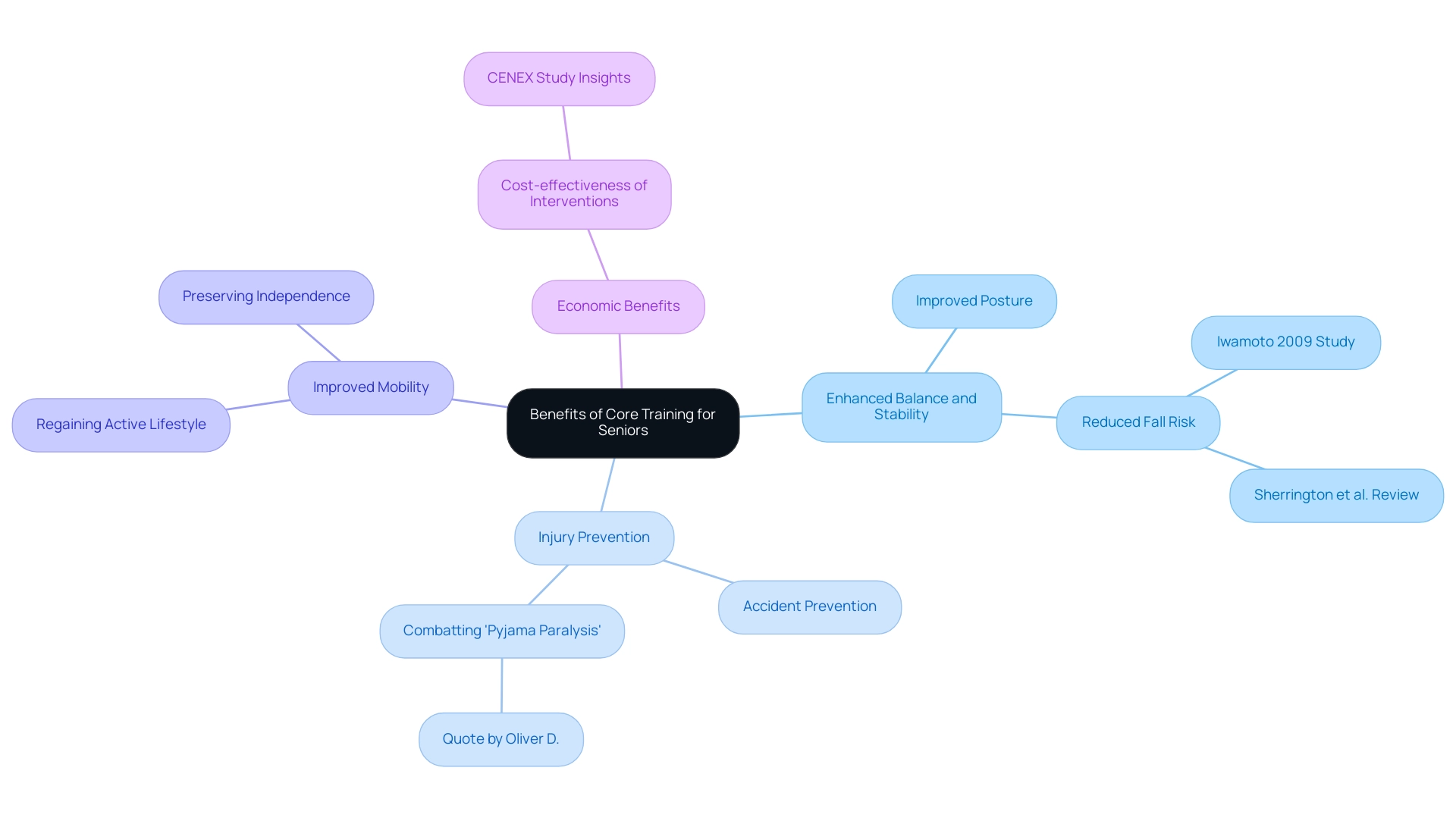
Core training serves as a core for seniors, playing a crucial role in enhancing their well-being, especially in improving balance and stability. Enhanced central strength, a vital aspect of core for seniors, results in improved posture, which is crucial for accident prevention and remains a primary source of injury among seniors. Studies show that older adults who participate in consistent strength training greatly reduce their risk of tumbling, as emphasized by Iwamoto's 2009 research on the protective benefits of physical activity against tumbles.
By incorporating core for seniors into their routines, seniors not only improve their mobility but also regain an active lifestyle, allowing them to preserve their independence. Oliver D. succinctly captures this urgency, emphasizing the need to combat 'pyjama paralysis' in hospital wards. Furthermore, recent systematic reviews, such as Sherrington et al.'s work in the Cochrane Database, emphasize the crucial importance of high-intensity resistance training in conjunction with fundamental workouts in significantly lowering fall risks, especially in older women with low bone mass.
The CENEX study also provides valuable insights into the economic aspects of these combined interventions, highlighting their cost-effectiveness in improving health outcomes for older adults. Thus, prioritizing workouts that focus on core for seniors is not just beneficial; it is essential for empowering our aging population, promoting a healthier, more active life, and ensuring that the economic benefits of such interventions are recognized.
Safety First: Guidelines for Seniors Performing Core Exercises
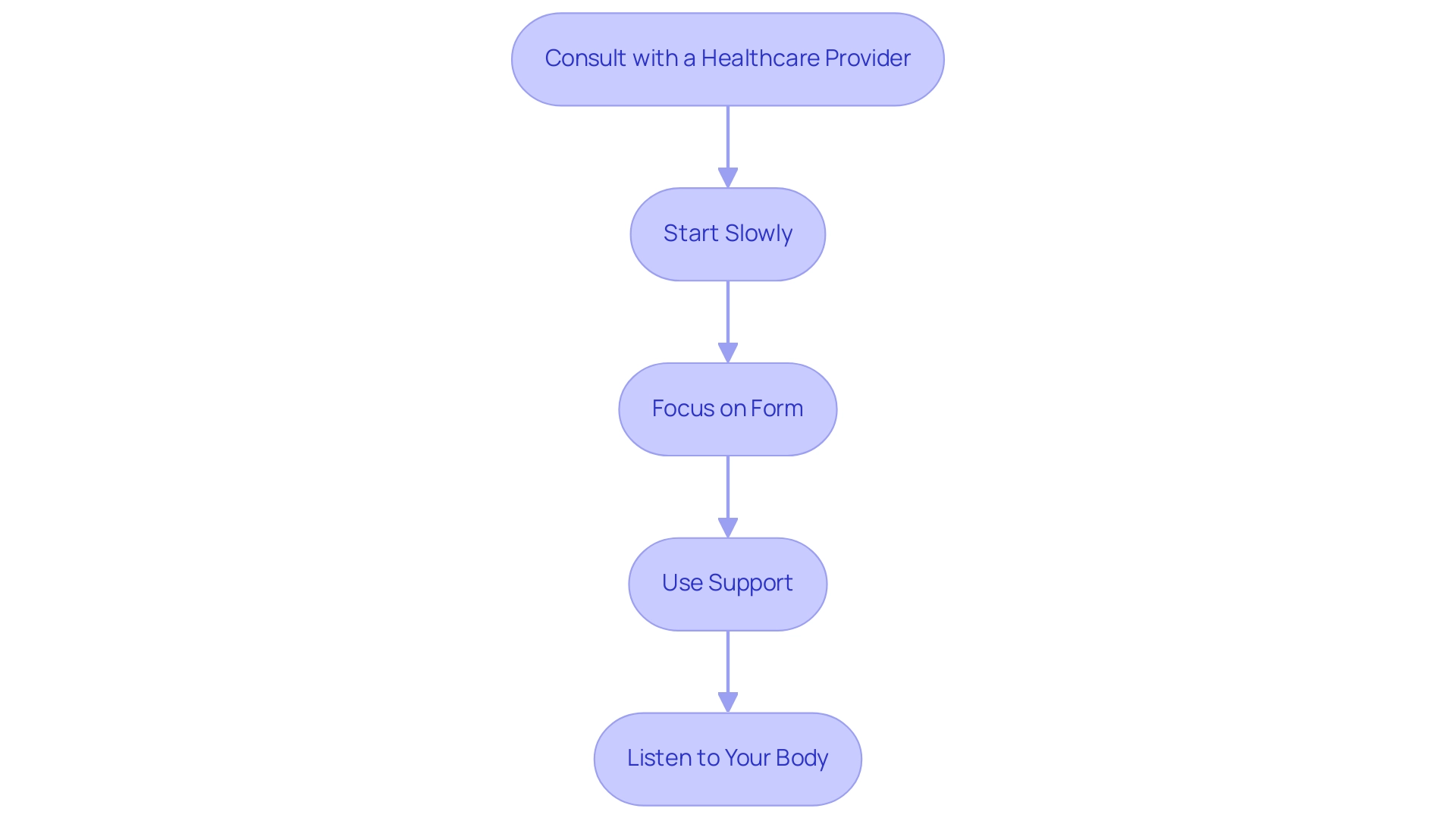
When participating in core workouts, older adults should prioritize safety by adhering to these essential guidelines:
- Consult with a Healthcare Provider: Before starting any new fitness regimen, it is crucial for seniors to consult their healthcare provider, especially if they have pre-existing health conditions. This step ensures they can safely participate in activities tailored to their needs. As Lisa Kahle mentions, 'The authors wish to express gratitude to Lisa Kahle for her programming support,' emphasizing the significance of expert guidance in training programs.
- Start Slowly: Embrace a gradual approach by beginning with low-intensity activities. As strength and confidence grow, seniors can progressively increase the complexity of their workouts, fostering a positive and empowering physical activity experience.
- Focus on Form: Maintaining proper form is vital to prevent injuries. Seniors should take their time, ensuring they perform activities correctly and safely, which also enhances overall effectiveness.
- Use Support: Incorporating support from sturdy objects like chairs or walls can significantly aid balance during exercises. This practice not only promotes safety but also encourages older adults to take confident steps in their fitness journey.
- Listen to Your Body: It's essential for older adults to listen to their bodies, recognizing the difference between normal muscle fatigue and pain that could indicate injury. Halting when discomfort occurs is essential for sustaining long-term health and wellness.
By following these recommendations, seniors can confidently and safely participate in core for seniors activities, creating a pathway for a healthier lifestyle. Notably, physical activity has been shown to reduce falls by 21%, underscoring the importance of safety in these activities. Furthermore, a case study examining trends in physical activity among older adults revealed that from 2007–08 to 2011–12, the proportion of older adults meeting guidelines increased from 21.7% to 27.2%, demonstrating the positive impact of participating in regular physical activity on overall health and quality of life.
Incorporating Core Exercises into Daily Life: Tips for Seniors
Integrating core for seniors workouts into everyday routines can greatly improve overall health and wellness for seniors, particularly given that expenses related to physical inactivity represent over 11% of total health care spending, estimated at $117 billion each year. Here are some actionable tips to inspire and guide this journey:
-
Set Realistic Goals: Establish achievable fitness objectives that allow for gradual progression.
This approach helps prevent frustration and encourages sustained commitment.
-
Schedule Workouts: Treat physical activity as a vital appointment by designating specific times for core workouts throughout the week.
Consistency is key to forming lasting habits.
-
Make it Social: Invite friends or family members to participate in workouts, transforming physical activity into a fun and enjoyable social event.
This not only boosts motivation but also fosters connections.
-
Use Reminders: Set notifications on phones or calendars to prompt workout sessions.
These nudges can help maintain focus and ensure that fitness remains a priority.
-
Celebrate Progress: Acknowledge and celebrate every achievement, no matter how small.
Acknowledging milestones strengthens motivation and dedication to fitness objectives.
Encouraging physical activity among older adults is an important public health issue, and by incorporating core for seniors movements into their daily routines, they can lead more active, fulfilling lives while enjoying the numerous advantages of physical activity. Effective workout alternatives include yoga, Pilates, aerobic activities such as walking and swimming, and low-impact strength training, which can be easily integrated into their schedules. As B. N. Balmain noted, understanding the implications of exercise is crucial for supporting elderly individuals in overcoming challenges and enhancing their well-being.
Conclusion
Core strength is not merely an aspect of fitness; it is a lifeline for seniors, directly influencing their stability, mobility, and overall quality of life. By understanding the critical role that a strong core plays in fall prevention and independence, HR Benefits Managers can advocate for exercise regimens that empower older adults. Effective core exercises, such as seated leg lifts and wall push-ups, have been shown to enhance balance and coordination, ultimately reducing the risk of falls that can lead to serious injuries.
Safety should always be paramount when seniors engage in core-strengthening activities. By following essential guidelines—consulting healthcare providers, prioritizing proper form, and listening to their bodies—seniors can confidently embark on their fitness journeys. Incorporating these exercises into daily routines not only promotes physical health but also fosters a sense of accomplishment and community among participants.
As the population ages, the need for targeted interventions grows. By prioritizing core strength, organizations can significantly impact the well-being of older adults, enhancing their independence and quality of life. With strategic implementation and support, the benefits of core training can create a healthier, more active generation of seniors, paving the way for a future where they can thrive.




