Overview
The article provides a comprehensive comparison of stomach fat and loose skin, exploring their distinct causes, health implications, and potential solutions. It emphasizes that stomach fat, particularly visceral fat, presents significant health risks. These risks can be effectively mitigated through lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise. Conversely, loose skin primarily impacts aesthetic concerns and self-esteem, often necessitating different management and treatment approaches.
Introduction
In the pursuit of a healthier body and enhanced self-esteem, grasping the intricacies of stomach fat and loose skin is essential. Stomach fat, particularly visceral fat, presents serious health risks, including cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Conversely, loose skin often arises as a cosmetic concern following significant weight loss or aging.
The relationship between these two conditions not only influences physical health but also carries substantial psychological implications, affecting self-image and overall well-being. This article examines the definitions, causes, and effective strategies for managing both stomach fat and loose skin, presenting a holistic approach that underscores the significance of:
- Lifestyle modifications
- Dietary choices
- Targeted interventions
By delving into these critical aspects, individuals can make informed decisions on their health journeys, ultimately achieving their aesthetic and wellness aspirations.
Understanding Stomach Fat and Loose Skin: Definitions and Differences
Stomach fat, commonly referred to as abdominal fat, is primarily classified into two distinct types: subcutaneous fat and visceral fat. Subcutaneous fat resides just beneath the surface, while visceral fat is located deeper, enveloping vital internal organs. This differentiation is crucial, as visceral fat is associated with heightened risks, including cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
In contrast, loose tissue is marked by a loss of elasticity and firmness, often resulting from significant weight loss, aging, or rapid weight fluctuations. While comparing stomach fat and loose skin presents tangible risks to well-being, loose skin primarily impacts aesthetic concerns and self-esteem.
Expert opinions underscore the importance of understanding these distinctions. For instance, research indicates that visceral fat is more responsive to lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, making it comparatively easier to lose than subcutaneous fat. A study from the Women's Health Initiative revealed that participants in an intervention group experienced a mean weight decrease of 2.2 kg within the first year, highlighting the effectiveness of targeted wellness strategies.
Additionally, F.X. noted that the trends in abdominal fat composition and distribution from 2011 to 2018 were concave but not linear, providing further context to the discussion on fat types. The prevalence of subcutaneous versus visceral fat varies across demographic groups, with statistical significance observed in trends related to visceral adipose tissue (VAT) percentages.
Understanding these trends is vital for tailoring health interventions that effectively address specific populations.
Moreover, the psychological effects of loose tissue warrant attention. Research indicates that individuals with loose tissue often experience diminished self-esteem, which can adversely affect their overall quality of life. A case study titled "Visceral Fat and Health Risks" emphasizes that visceral fat is easier to lose than subcutaneous fat and can be reduced through a healthy lifestyle that includes diet and exercise.
This highlights the importance of maintaining a nutritious diet and consistent exercise to prevent the accumulation of visceral fat, thereby minimizing risks and enhancing overall well-being.
In summary, distinguishing between stomach fat and loose skin is essential for implementing effective wellness strategies. By understanding the unique characteristics and consequences of each condition, individuals can make informed choices regarding their health and aesthetic goals. Furthermore, partnerships like those offered by Foresight Health Coaching present organizations with opportunities to cultivate a healthier, happier, and more cohesive team culture.
Foresight Health Coaching's personalized health coaching and corporate wellness programs are designed to assist individuals in managing their health effectively, emphasizing the significance of health interventions in corporate wellness initiatives.
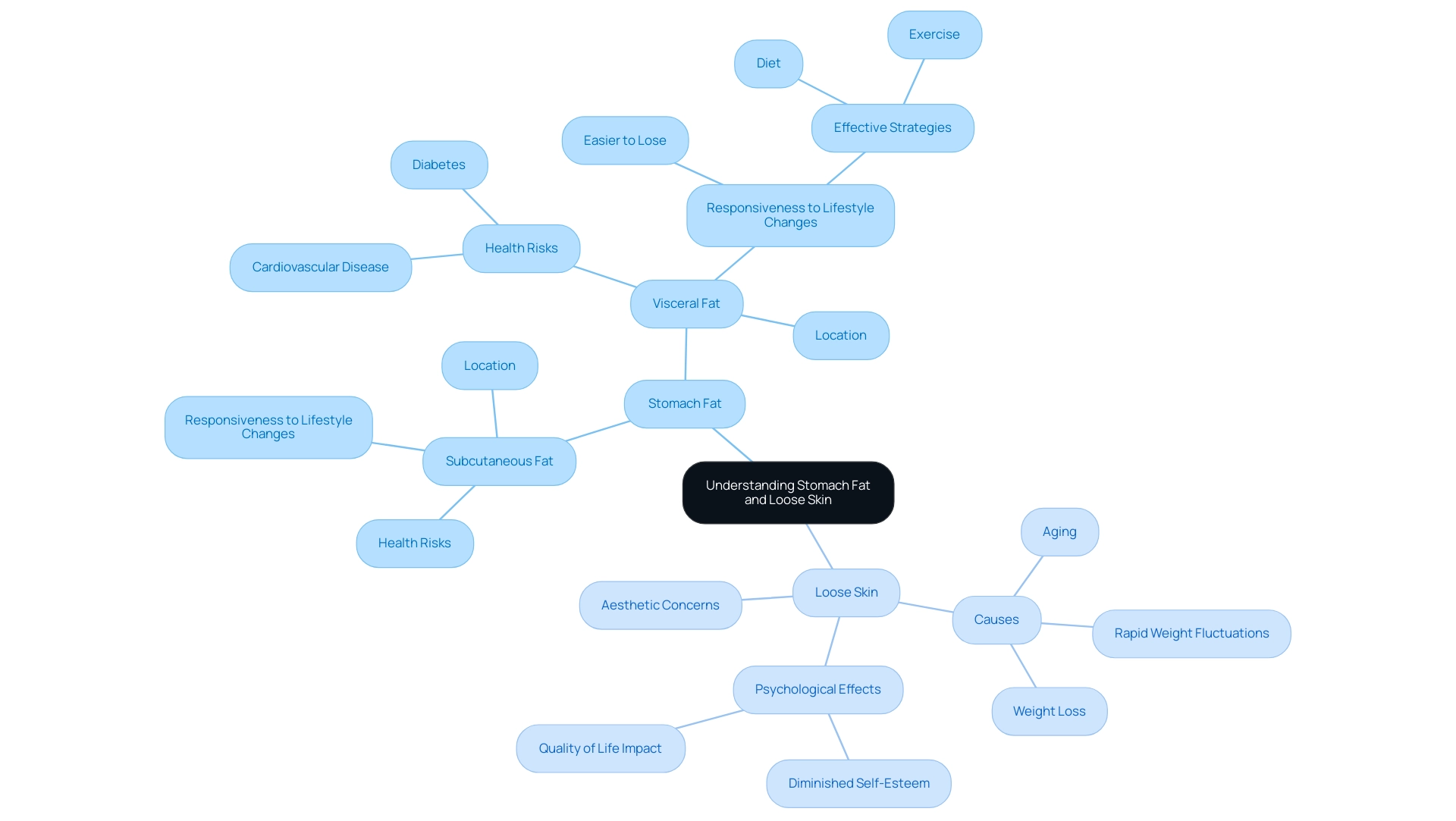
Causes of Stomach Fat: Factors Contributing to Excess Weight
Stomach fat accumulation is influenced by a multitude of factors, including dietary habits, physical activity levels, hormonal fluctuations, and genetic predispositions. A significant contributor to excess abdominal fat is the consumption of high-calorie diets, particularly those laden with sugars and unhealthy fats. Research indicates that individuals with diets high in refined carbohydrates and low in soluble fiber are at a greater risk for abdominal fat accumulation.
In fact, studies have shown that increasing soluble fiber intake can help mitigate this risk, particularly in high-risk populations. Furthermore, it has been noted that increased soluble fiber intake and vigorous physical activity may help slow the progression of abdominal fat accumulation in these groups.
Moreover, the role of physical activity cannot be overstated. Regular exercise has been linked to improved regulation of free fatty acid (FFA) metabolism, which is crucial for managing body fat distribution. Engaging in vigorous physical activity not only aids in weight management but also helps in redistributing fat away from the abdominal area.
Experts propose that aerobic exercise is especially effective in this regard, as it encourages fat loss while improving overall metabolic function. As James de Lemos, M.D. states, "Aerobic exercise is more effective than resistance training at distributing fat to the best places in the body, but both are beneficial."
Hormonal changes, often exacerbated by stress, also play a critical role in stomach fat accumulation. Stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which are associated with increased fat storage in the abdominal region. Understanding the interplay between stress, hormones, and fat distribution is vital for developing effective weight management strategies.
Genetics further complicates the picture, as some individuals may be predisposed to store fat in the abdominal area more than others. This genetic factor, coupled with lifestyle choices, highlights the significance of a holistic approach to well-being.
Case studies have demonstrated that dietary interventions can significantly impact stomach fat accumulation. For instance, research indicates that upper body/visceral fat distribution in obesity is closely associated with metabolic complications, while increased lower body fat is linked to reduced cardiovascular risk. Individuals who adopted a balanced diet rich in whole foods and engaged in regular physical activity reported notable reductions in abdominal fat over time.
These findings highlight the necessity of addressing both diet and exercise in any effective weight management program.
In summary, addressing the issue of stomach fat versus loose skin requires a multifaceted approach that considers dietary choices, physical activity, hormonal influences, and genetic factors. By understanding these elements, individuals can develop targeted strategies to reduce abdominal fat and enhance their overall health.
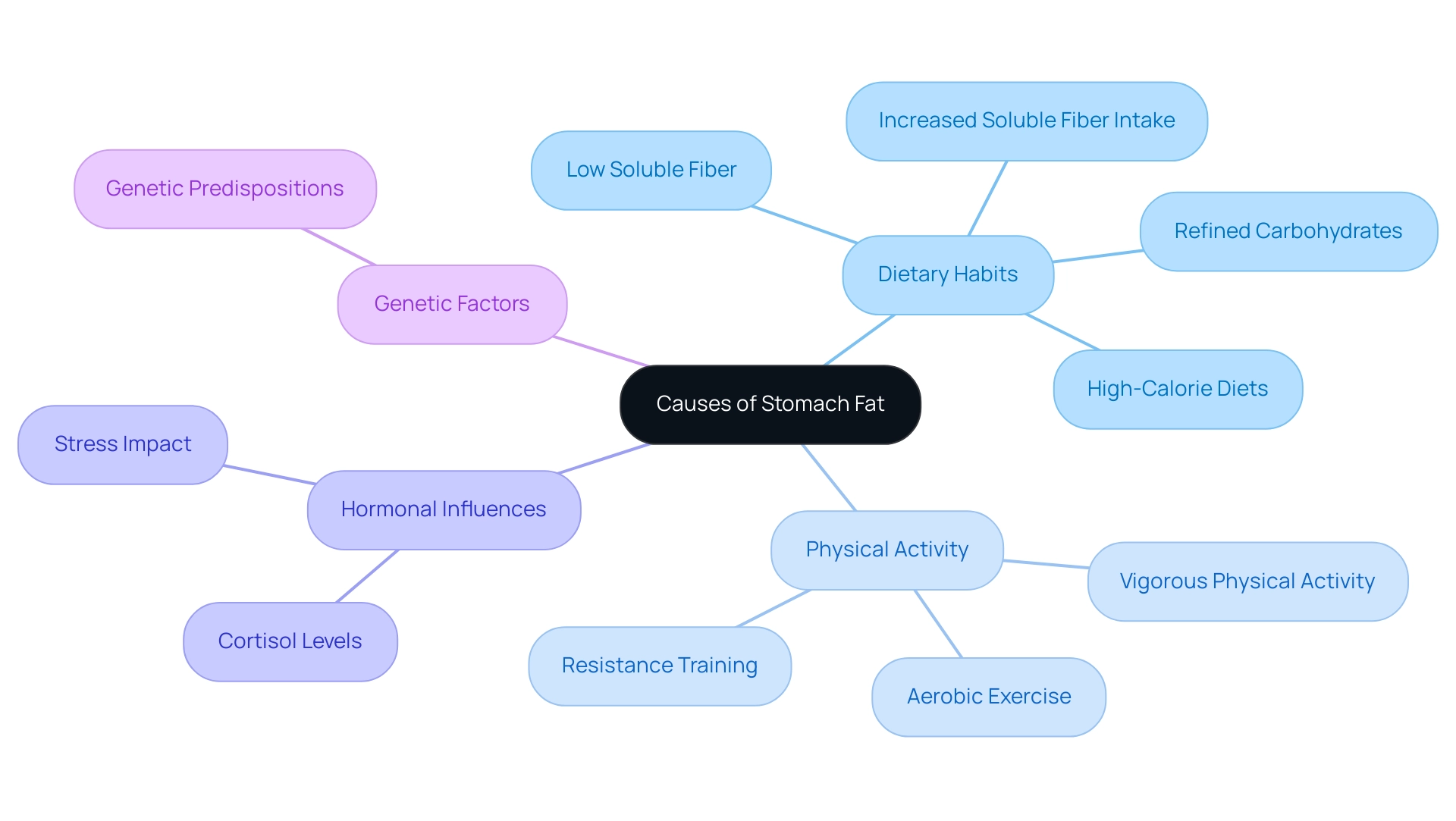
Understanding Loose Skin: Causes and Contributing Factors
Following significant weight loss, pregnancy, or the natural aging process, many individuals grapple with the concerns surrounding stomach fat versus loose skin. The rapid stretching of the skin—often seen during pregnancy or obesity—can diminish its elasticity, leading to challenges in retraction after weight loss. This issue is notably pronounced among those who undergo substantial weight fluctuations, highlighting the ongoing debate of stomach fat versus loose skin.
Research underscores the impact of aging on skin elasticity, revealing that collagen production declines over time, resulting in diminished firmness and resilience of the tissue. Statistics indicate that the expression of collagen XIV decreases in individuals post-bariatric surgery, emphasizing the hurdles faced in maintaining skin tightness after weight loss.
Genetics also plays a pivotal role in determining the elasticity of the outer layer. Some individuals may possess a genetic predisposition for more resilient tissue, while others may experience a more pronounced loose texture following weight loss. Furthermore, environmental factors, such as sun exposure, can exacerbate the loss of elasticity, making it crucial for individuals to consider these aspects when addressing their concerns.
Experts advocate for several strategies to mitigate laxity during weight loss:
- Progressive weight reduction
- Strength exercises
- A balanced diet
These essential components can help preserve elasticity and promote overall dermal health. Case studies from Foresight Health Coaching's corporate wellness programs demonstrate that individuals adhering to these guidelines not only enhance their chances of achieving firmer skin but also improve their physical appearance and self-esteem.
Investing in wellness initiatives allows organizations to support their employees in maintaining both physical health and dermal integrity.
Understanding the multifaceted causes of sagging tissue is vital for those seeking effective solutions regarding stomach fat versus loose skin. As Thomas Inge, a consultant for Standard Bariatrics, states, "The authors have nothing to disclose with the exception of Thomas Inge who is a consultant for Standard Bariatrics." This underscores the importance of professional guidance in exploring options for dermal health.
Moreover, while excess tissue removal procedures are primarily aesthetic, they can be medically necessary in certain situations, providing individuals with additional choices to consider.
By acknowledging the interplay of age, genetics, and lifestyle factors, individuals can make informed decisions about their weight loss journeys, particularly when contemplating stomach fat versus loose skin.
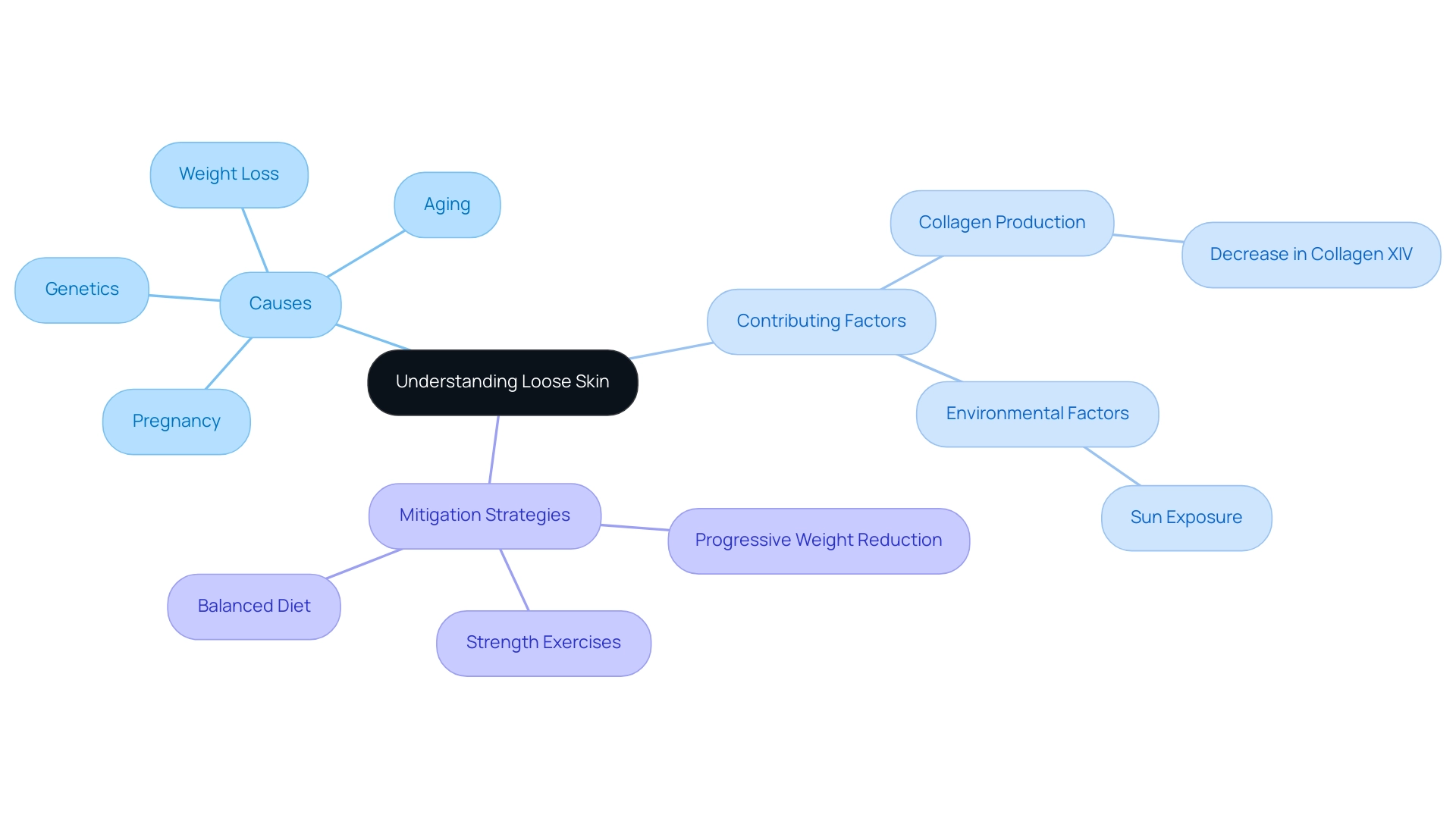
Health Risks of Stomach Fat and Loose Skin: What You Need to Know
Excess stomach fat, particularly visceral fat, poses significant health risks, including an increased likelihood of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Research indicates that a hip-to-waist ratio exceeding 0.85 in women and 0.90 in men often signifies higher visceral fat levels, exacerbating these health concerns. While loose tissue may not directly endanger physical health, it can lead to complications such as irritation and infections.
More critically, individuals may experience psychological distress stemming from body image issues, which can adversely affect overall well-being.
The psychological impacts of loose tissue are profound. Studies show that individuals frequently report feelings of embarrassment and diminished self-esteem. This emotional burden can lead to social withdrawal and anxiety, complicating one's relationship with their body. Understanding these risks is essential for individuals, highlighting the importance of effectively managing stomach fat versus loose skin.
Moreover, expert opinions underscore the dangers of visceral fat. Medical professionals emphasize its role in various chronic conditions. J H Pinthus, MD, PhD, stresses the clinical significance of visceral adiposity, stating, "A critical review of methods for visceral adipose tissue analysis is essential for understanding its implications for well-being." This underscores the need for increased awareness and proactive measures to mitigate the risks associated with visceral fat.
Incorporating personalized coaching into workplace wellness programs can significantly address both the physical and psychological aspects of these conditions. Experienced coaches, such as those from Corporate Membership - Contact Our Health Coaches Today, provide tailored support and guidance, empowering individuals to make lasting lifestyle changes. For instance, one client shared, "Working with my coach transformed my approach to wellness; I feel more confident and in control of my body than ever before."
A case study titled "Impact of Exercise on Workplace Performance" indicates that regular physical activity enhances job performance, creativity, and stress management. By fostering a culture of wellness through partnerships with experienced wellness coaches, organizations can empower employees to manage their risks effectively, leading to improved overall well-being and a more cohesive team culture.
To take the first step towards improving your health and quality of life, contact Corporate Membership - Contact Our Health Coaches Today for personalized support and guidance tailored to your needs.
Effective Strategies for Reducing Stomach Fat: Diet and Exercise Tips
To effectively reduce stomach fat versus loose skin, individuals should prioritize a balanced diet that emphasizes whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Research indicates that diets rich in these components can lead to significant reductions in body weight and waist circumference. Furthermore, regular consumption of green tea has also been linked to reductions in body weight and waist circumference, further supporting dietary strategies for fat loss.
Regular physical activity is equally crucial. Incorporating both aerobic exercises and strength training can substantially enhance fat loss efforts. For instance, studies show that individuals who engage in exercise at least three times a week experience improved job performance and creativity, which can be beneficial in a corporate setting.
Moreover, managing stress through mindfulness practices is essential, as it helps regulate hormones that contribute to fat accumulation. This multifaceted approach not only promotes weight loss but also addresses the concerns of stomach fat versus loose skin, fostering overall well-being and leading to a more cohesive and resilient team culture.
Successful corporate wellness programs, such as the partnerships offered by Foresight Health Coaching, have demonstrated reductions in absenteeism and increased employee satisfaction, further underscoring the importance of a healthy lifestyle. By investing in such partnerships, organizations can enhance their teams' well-being and productivity, as evidenced by the diverse range of businesses that Foresight Health Coaching has collaborated with, showcased through their logos.
Incorporating these strategies can lead to effective fat loss, especially when considering stomach fat versus loose skin, and improved wellness outcomes. It is imperative for organizations to invest in their teams' wellness. As Apichart Vanavichit observed, collaborative efforts in well-being initiatives are crucial for success. By doing so, organizations not only enhance personal health but also cultivate a more productive and engaged workforce.
Additionally, intermittent fasting is a popular weight loss method that can complement these dietary strategies, providing a broader perspective on effective approaches to fat loss.
Addressing Loose Skin: Non-Surgical and Surgical Treatment Options
Addressing treatment options for stomach fat versus loose skin encompasses a spectrum of approaches, each meticulously tailored to the severity of the condition. Non-surgical methods—such as tightening creams, laser treatments, and radiofrequency therapy—often prove effective for individuals experiencing mild to moderate laxity. These treatments stimulate collagen production and enhance elasticity, providing a less invasive solution with minimal downtime.
However, as Jessica Weiser, MD, FAAD, notes, "For patients with severe laxity of the lower face, neck, and eyes, nonsurgical treatments are sometimes not adequate to fully correct these concerns."
For those grappling with considerable excess tissue, surgical interventions like tummy tucks and body lifts are typically recommended. These procedures deliver more dramatic results, effectively removing excess tissue and tightening the underlying layers. Research indicates that surgical options for tightening yield high success rates, with many patients reporting substantial improvements in both appearance and self-esteem.
Expert opinions underscore the importance of individualized treatment plans. A qualified expert can evaluate the level of laxity and suggest the most suitable approach. This is where personalized coaching—such as that offered by Corporate Membership—becomes invaluable.
Experienced coaches utilize evidence-based techniques to guide individuals in making lasting lifestyle changes that enhance overall health, including dermal health. For instance, one client mentioned, "The coaching I received helped me understand my body better and make changes that enhanced my complexion."
Recent studies have demonstrated that non-surgical treatments for sagging tissue, such as infrared therapy, can yield noticeable enhancements after a series of sessions, typically three to six. Patients may experience mild discomfort post-treatment, yet the results can be significant, enhancing texture and firmness. This aligns with findings from case studies on workplace exercise programs, which illustrate that promoting a culture of wellness can lead to improved employee satisfaction and productivity.
In summary, the choice between non-surgical and surgical options for addressing concerns such as stomach fat versus loose skin should be guided by the specific needs and conditions of the individual. By consulting with skilled experts, patients can make informed choices that align with their aesthetic aspirations and wellness considerations. Moreover, programs such as those provided by Corporate Membership can play a vital role in promoting overall wellness, essential for preserving dermal condition and boosting employee morale.
Contact us today to start your journey towards a healthier you!
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Stomach Fat and Loose Skin: A Holistic Approach
Effectively managing stomach fat versus loose skin requires a comprehensive approach that includes regular exercise, a nutritious diet, and sufficient hydration. Studies indicate that lifestyle changes can lead to significant reductions in abdominal fat, enhancing not only physical appearance but also metabolic function. For example, a study titled "Impact of Lifestyle Intervention on Abdominal Fat" demonstrated a correlation between lifestyle modifications and decreased circulating glycerol levels, suggesting that such interventions can effectively target stomach fat.
Moreover, lifestyle interventions that reduce belly fat have been shown to lower the risk of the most common type of heart failure in older adults, highlighting the critical importance of these changes.
Hydration is essential for maintaining dermal elasticity. Statistics reveal that individuals who prioritize hydration tend to have improved skin conditions, as adequate water intake supports cellular function and elasticity. Additionally, sleep is a crucial factor in this equation; research shows that quality sleep aids in skin repair and rejuvenation, thus enhancing overall skin appearance.
Incorporating stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can further bolster well-being. These practices not only promote mental health but also support physical health by reducing cortisol levels, which are associated with fat accumulation. As Chika Anekwe, MD, MPH, notes, "As a nation, we must tackle these challenges and discover systemwide solutions for reducing socioeconomic barriers and eradicating racism, in order to enhance personal agency and capability to lead healthier lives."
By embracing these holistic lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly enhance their physical appearance and overall quality of life, particularly in addressing the challenges of stomach fat versus loose skin, fostering a healthier, more vibrant self. Furthermore, Foresight Health Coaching's partnership promotes a healthier, happier, and more cohesive team culture, making these lifestyle changes advantageous not only for individuals but also for organizations.
Key Takeaways: Navigating the Journey from Stomach Fat to Firm Skin
Understanding the distinctions between stomach fat and loose skin is essential for effectively addressing these conditions. Stomach fat, often associated with various risks such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes, can be influenced by lifestyle choices, including diet and physical activity. Research indicates that individuals who engage in regular exercise—specifically, at least 30 minutes three times a week—report higher motivation levels at work, translating into a more active lifestyle overall.
Corporate Membership - Contact Our Wellness Coaches Today plays a crucial role in fostering a culture of well-being and unity within teams. This initiative encourages individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles through personalized support and experienced coaching. Such guidance is essential for making enduring lifestyle changes that significantly affect wellness outcomes. Our experienced coaches utilize evidence-based techniques to ensure that clients receive the most effective support tailored to their unique needs.
Conversely, loose tissue typically results from significant weight loss or aging, leading to a decrease in elasticity. This condition can impact self-esteem and body image, making it crucial to explore effective treatment options alongside the comparison of stomach fat versus loose skin reduction strategies. A holistic approach that integrates dietary changes, physical activity, and personal care can yield significant enhancements in both well-being and appearance.
For instance, a comprehensive study involving over 120,000 participants revealed that lifestyle factors, including increased physical activity and a diet rich in vegetables and whole grains, are associated with weight loss. In contrast, high consumption of processed foods correlates with weight gain. This underscores the importance of making informed dietary choices as part of a broader strategy to manage stomach fat versus loose skin and improve skin health. Reducing stomach fat not only enhances physical appearance but also boosts self-esteem and overall mental well-being.
As wellness expert Lyudmyla Kompaniyets emphasizes, clinicians and public initiatives can concentrate on interventions aimed at clinically meaningful weight loss (i.e., ≥5%) for adults at any level of excess weight. By nurturing a culture of well-being and unity within teams, organizations can inspire individuals to adopt these lifestyle changes, ultimately resulting in a more robust, resilient workforce. Testimonials from our clients highlight the transformative impact of our coaching services, showcasing real-life success stories that inspire others to take control of their health journey.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of stomach fat and loose skin is crucial for anyone on a journey toward improved health and self-esteem. Stomach fat, particularly visceral fat, poses significant health risks, while loose skin can affect one's body image and emotional well-being. Key strategies for managing these conditions include:
- Making informed dietary choices
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Considering both non-surgical and surgical options for skin tightening
A holistic approach that integrates lifestyle modifications, such as stress management and hydration, can yield remarkable results. Evidence suggests that individuals who adopt healthier habits not only reduce their abdominal fat but also enhance their skin elasticity, leading to improved physical appearance and overall quality of life. Furthermore, organizations that support wellness initiatives foster a culture of health, empowering their employees to thrive both personally and professionally.
Ultimately, the journey from managing stomach fat to achieving firmer skin is multifaceted. By understanding the underlying factors and implementing targeted strategies, individuals can transform their health trajectories, boost their self-esteem, and cultivate a resilient mindset. Embracing these changes is not just about aesthetics; it’s about nurturing a healthier, happier self, paving the way for a more fulfilling life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the two main types of stomach fat?
The two main types of stomach fat are subcutaneous fat, which lies just beneath the skin, and visceral fat, which is located deeper and surrounds vital internal organs.
Why is visceral fat considered more concerning than subcutaneous fat?
Visceral fat is associated with heightened risks for serious health issues, including cardiovascular disease and diabetes, making it more concerning than subcutaneous fat.
What is loose tissue, and what causes it?
Loose tissue is characterized by a loss of elasticity and firmness, often resulting from significant weight loss, aging, or rapid weight fluctuations.
How do stomach fat and loose skin differ in terms of health impacts?
While both stomach fat and loose skin can have health implications, loose skin primarily affects aesthetic concerns and self-esteem, whereas stomach fat is linked to more serious health risks.
Can visceral fat be lost more easily than subcutaneous fat?
Yes, research indicates that visceral fat is more responsive to lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, making it easier to lose compared to subcutaneous fat.
What role does diet play in stomach fat accumulation?
Diet significantly influences stomach fat accumulation, with high-calorie diets, especially those rich in sugars and unhealthy fats, contributing to excess abdominal fat. Increasing soluble fiber intake can help mitigate this risk.
How does physical activity affect stomach fat?
Regular physical activity improves the metabolism of free fatty acids and aids in weight management, helping to redistribute fat away from the abdominal area. Aerobic exercise is particularly effective for fat loss.
What hormonal factors are involved in stomach fat accumulation?
Hormonal changes, particularly stress-induced increases in cortisol levels, can lead to greater fat storage in the abdominal region.
How do genetics influence stomach fat distribution?
Genetics can predispose some individuals to store fat in the abdominal area more than others, highlighting the need for a holistic approach to weight management that considers both genetic and lifestyle factors.
What strategies can individuals adopt to reduce abdominal fat?
Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress are effective strategies for reducing abdominal fat and enhancing overall health.

