Overview
Eating 1400 calories a day can be an effective and safe strategy for women aiming for weight loss while maintaining essential nutrient intake, particularly when combined with regular physical activity. The article supports this by highlighting the importance of nutrient-dense foods, personalized meal planning, and monitoring health responses, which collectively help ensure that the diet is sustainable and meets individual health needs.
Introduction
In the quest for effective weight management, many women are turning to the 1400-calorie diet as a strategic approach to shed pounds while ensuring they receive essential nutrients. This dietary plan not only emphasizes caloric control but also highlights the significance of balanced nutrition, making it a viable option for those engaged in moderate physical activity.
By understanding the delicate interplay between caloric intake and energy expenditure, individuals can tailor their eating habits to suit their unique needs. From meal planning to food choices, this diet offers a structured framework that promotes mindful eating and portion control, paving the way for sustainable weight loss and improved overall well-being.
However, as with any dietary regimen, it's crucial to navigate this journey with a focus on health and personalization, ensuring that the path to weight loss does not compromise nutritional integrity.
Understanding the 1400-Calorie Diet for Women
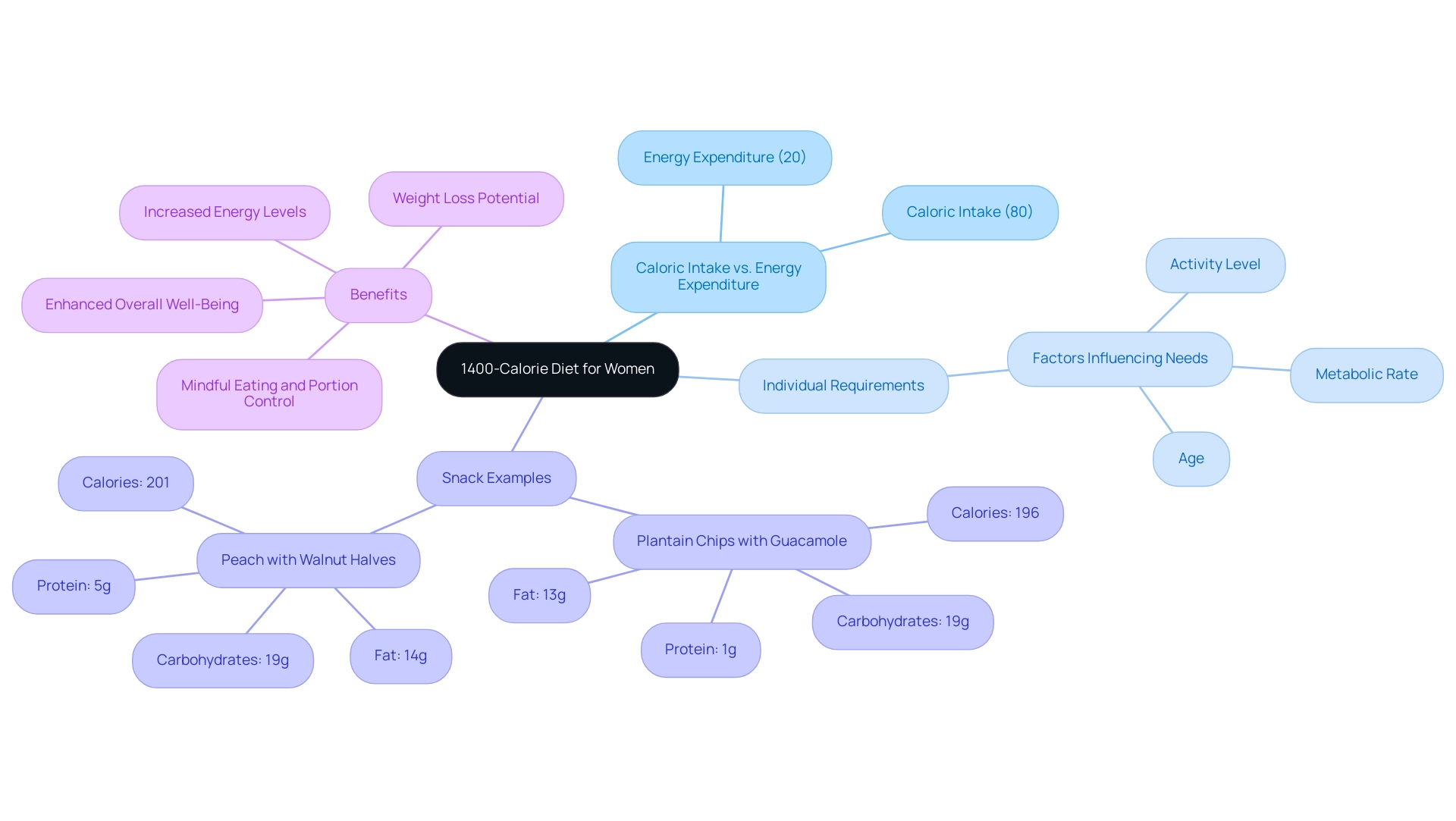
Eating 1400 calories a day female is an effective strategy for women aiming to control their body mass while ensuring they receive essential nutrients. This caloric limit is particularly beneficial for those who engage in moderate physical activity. A key aspect of this diet is understanding the relationship between caloric intake—where approximately 80% of mass is determined—and energy expenditure, which accounts for the remaining 20%.
Individual requirements will differ based on factors such as age, activity level, and metabolic rate, highlighting the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional before embarking on any new dietary regimen. The benefits of eating 1400 calories a day female include potential weight loss and an increase in energy levels, contributing to enhanced overall well-being when followed appropriately.
For instance, a snack option like plantain chips with 1/4 cup of guacamole provides a balanced choice at 196 units, offering:
- 1 gram of protein
- 19 grams of carbohydrates
- 13 grams of fat
Additionally, a case study featuring a snack of a peach served with walnut halves totals 201 units of energy, with:
- 5 grams of protein
- 19 grams of carbohydrates
- 14 grams of fat
This illustrates practical application. Moreover, this approach encourages mindful eating and portion control, both of which are essential for achieving long-term success in managing body composition. It is also crucial to note that while tracking energy intake can be effective, focusing on a balanced diet rich in whole foods is essential for long-term health and weight management.
How to Plan Your Meals on a 1400-Calorie Diet
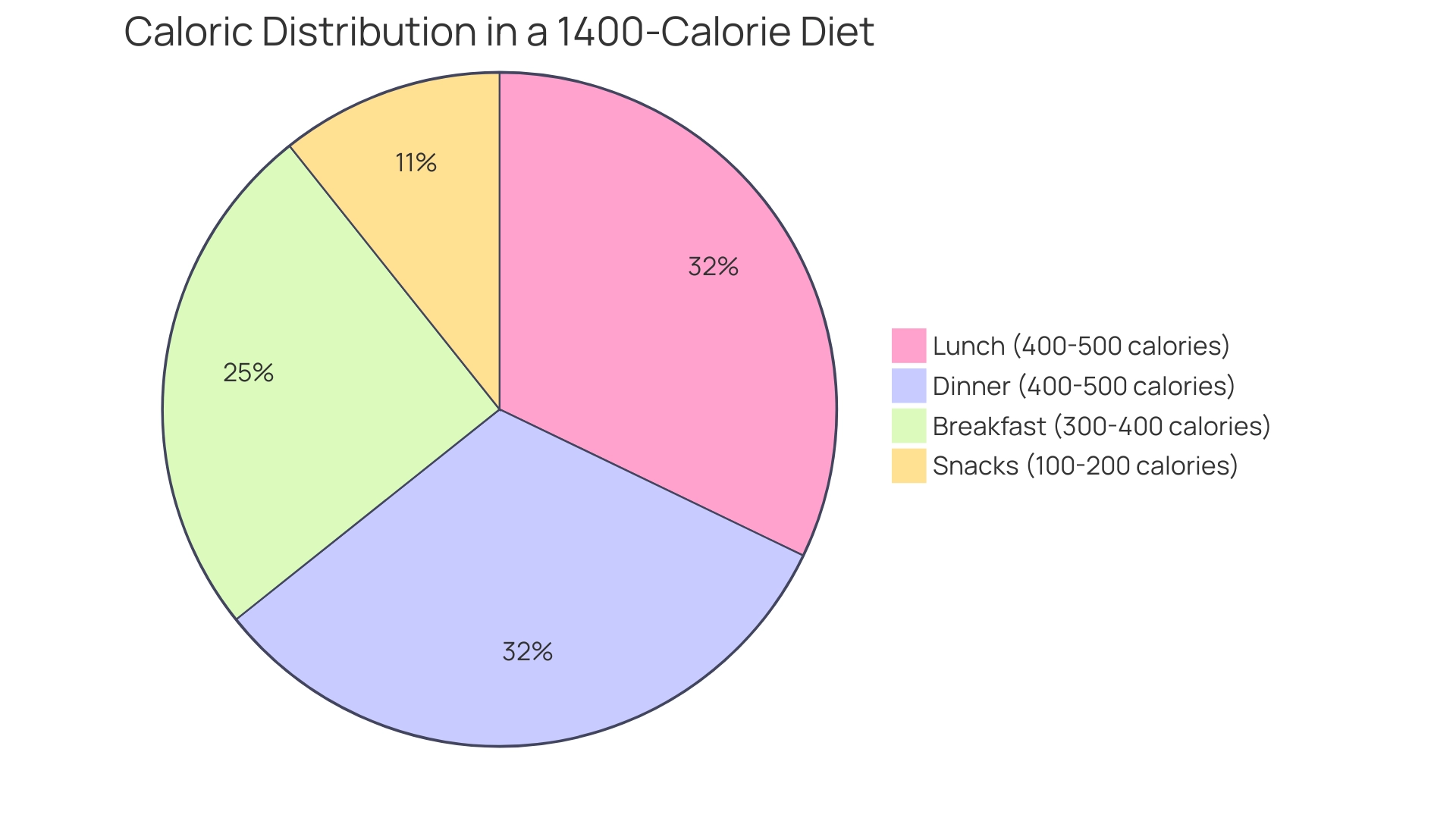
Effective meal planning for eating 1400 calories a day female begins with determining an appropriate caloric distribution for your daily intake. A practical approach involves allocating approximately:
- 300-400 units for breakfast
- 400-500 units for lunch
- 400-500 units for dinner
- 100-200 units for snacks
For instance, a salad lunch option can offer 381 energy units, 15 grams of protein, 38 grams of carbohydrates, and 20 grams of fat, making it a nutritious choice within this framework.
Using a dining planning app or a simple spreadsheet can streamline your process and help you maintain oversight of your weekly dishes. It's crucial to incorporate a diverse array of food groups, such as lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, to ensure nutritional adequacy. A healthy snack option could include:
- Plantain chips with guacamole, totaling 196 calories
- A peach with walnut halves, which has 201 calories
Preparing dishes in advance can significantly reduce time spent cooking during the week and help curb impulsive eating. Consider dedicating a few hours weekly for food preparation, which includes batch cooking and portioning dishes, to stay aligned with your caloric targets while enjoying a variety of flavors and nutrients. As noted by Rebecca Jaspan, MPH, RD, 'We recognize that eating 1400 calories a day female may not be appropriate for everyone, especially those with disordered eating habits.'
This emphasizes the significance of personalization in food planning. Furthermore, a dietitian's case study titled '1,500-Calorie Diet Plan for Shedding Pounds' illustrates that organized meal planning promotes successful fat reduction while maintaining nutritional balance. This organized method not only assists in attaining fitness objectives but also encourages a balanced consumption of essential nutrients.
Foods to Include for a Balanced 1400-Calorie Diet
A well-structured plan for eating 1400 calories a day female must encompass a diverse array of food groups to meet essential nutritional requirements. Prioritizing the inclusion of the following components is essential:
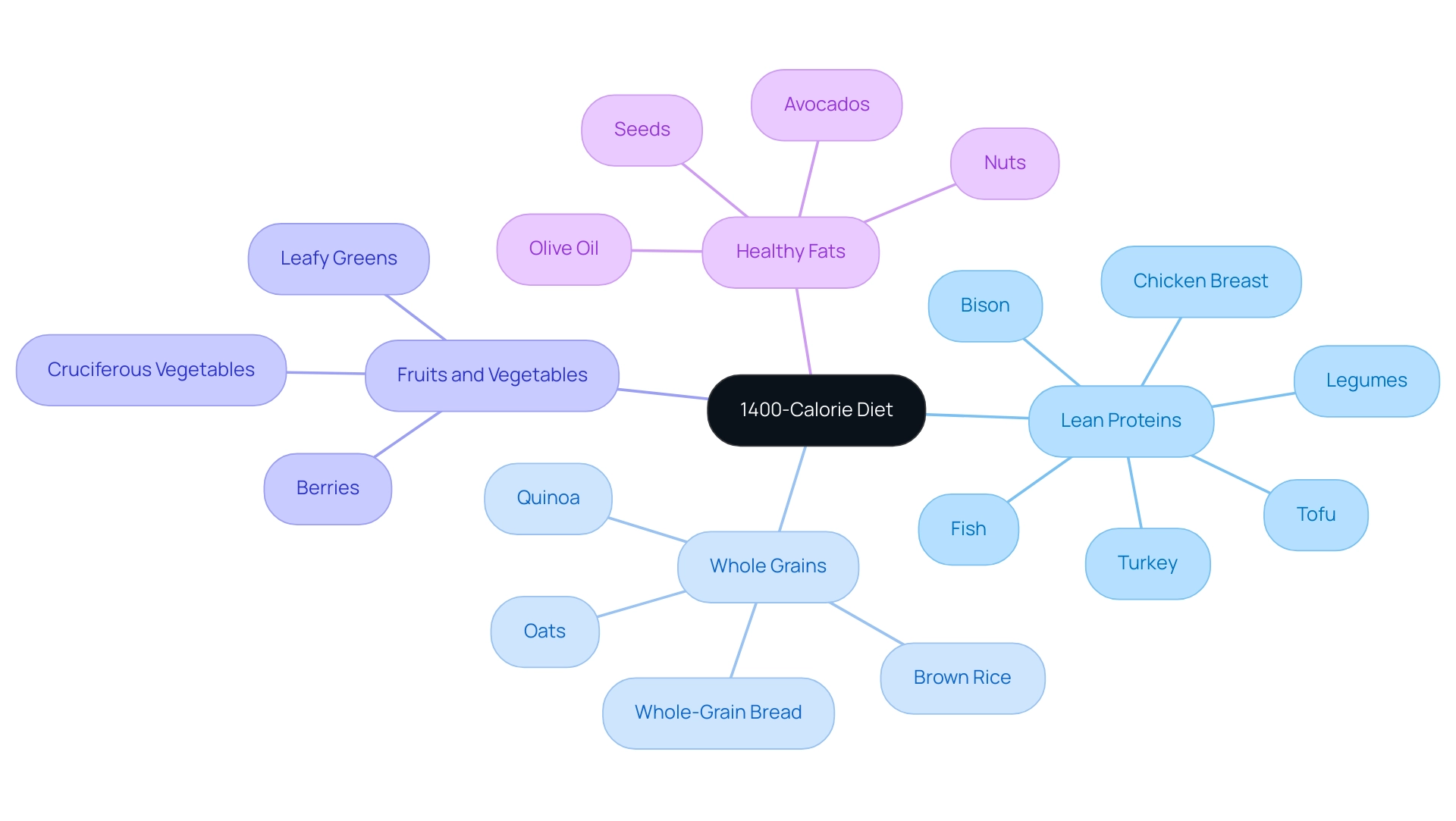
- Lean Proteins: Selections like chicken breast, turkey, fish, legumes, tofu, and especially, bison—known for being leaner than beef, with reduced energy content and less saturated fat—are outstanding options. According to recent studies, many protein-rich foods are also significant sources of micronutrients, such as iron in meat and calcium in dairy foods, so a diet rich in protein is hugely beneficial for our overall health. They offer the fullness required for reducing body mass while aiding muscle preservation.
- Whole Grains: Incorporating brown rice, quinoa, whole-grain bread, and oats is vital, as these foods are abundant in fiber and necessary nutrients. They not only contribute to a feeling of fullness but also regulate blood sugar levels, which is essential for sustained energy.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a colorful assortment, including berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables. These are low in calories and rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them ideal for maintaining health while adhering to a lower calorie intake.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporating sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil in moderation supports hormone regulation and overall health. These beneficial fats play an essential part in nutrient uptake and can improve the appeal of dishes.
By varying food selections while eating 1400 calories a day female, you can enjoy fulfilling dishes that ensure you receive adequate nutrition while supporting your weight loss goals. Additionally, the timing and composition of meals, particularly protein intake, can impact performance and recovery, making it essential to consider protein consumption before and after workouts.
Foods to Avoid on a 1400-Calorie Diet
To optimize the success of eating 1400 calories a day female, it’s vital to steer clear of specific foods that can undermine your weight loss goals. Key offenders include:
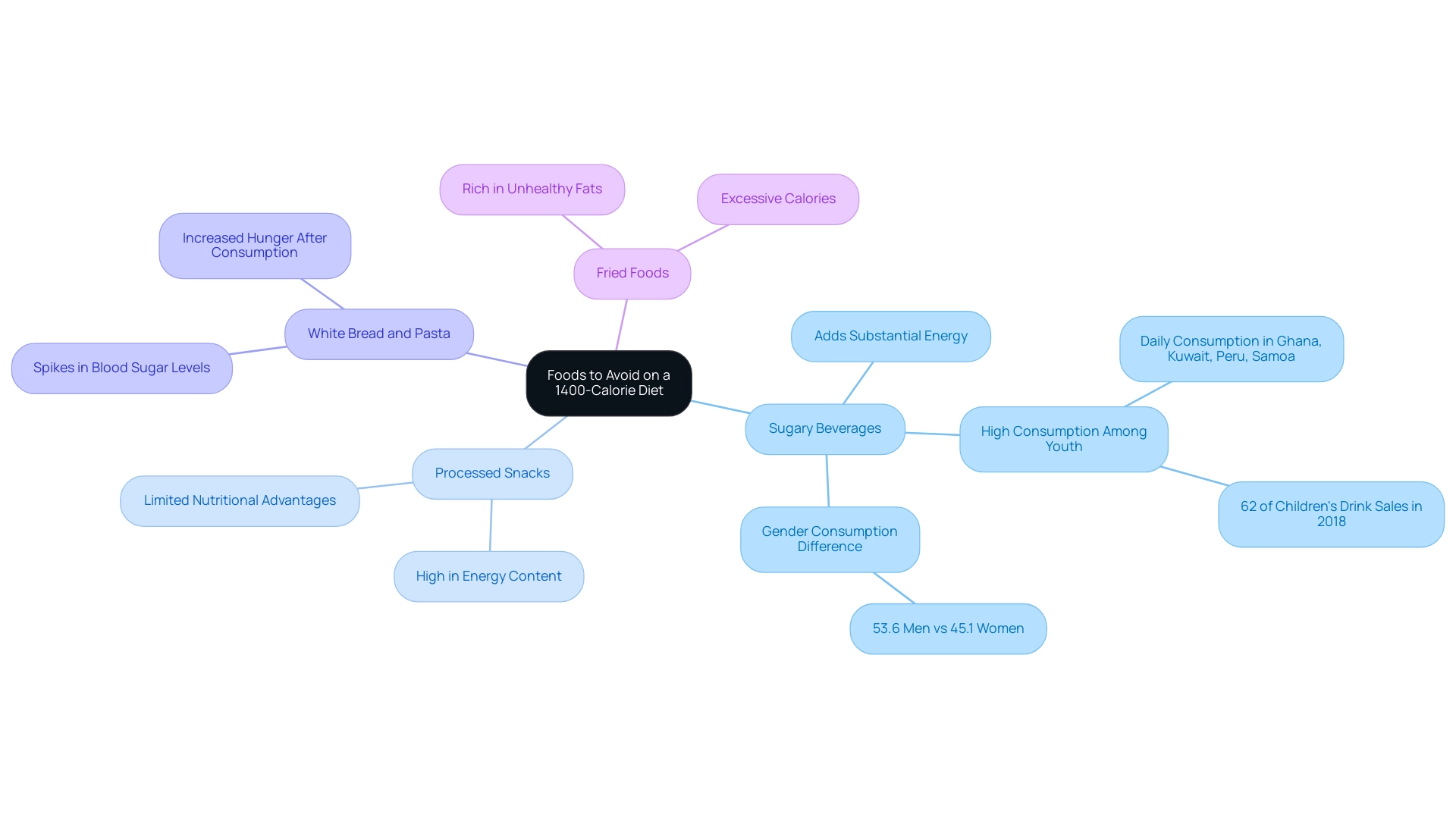
- Sugary Beverages: Items such as sodas, energy drinks, and sweetened teas are notorious for adding substantial energy without contributing to feelings of fullness. Surveys indicate that the majority of children and adolescents consume at least one portion of sugar-sweetened beverages daily in countries like Ghana, Kuwait, Peru, and Samoa. A 2019 analysis revealed that children aged 2-11 were exposed to twice as many advertisements for sugary drinks compared to healthier options, resulting in these beverages accounting for 62% of their drink sales in 2018. Notably, a higher percentage of men (53.6%) than women (45.1%) reported consuming at least one sugar-sweetened beverage daily, highlighting a widespread dietary concern. As Dr. Asher Rosinger observes, this consumption pattern presents considerable dangers to energy intake and general health.
- Processed Snacks: Snacks such as chips, cookies, and candies are usually high in energy content while offering limited nutritional advantages, resulting in elevated energy intake and possible overeating.
- White Bread and Pasta: Refined grains can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels, causing increased hunger shortly after consumption. Opting for whole grains can help maintain satiety and stabilize energy levels.
- Fried Foods: Rich in unhealthy fats and excessive calories, fried foods can easily push your intake beyond your caloric target. Instead, prefer baked or grilled options to assist in sustaining a healthier diet.
By intentionally steering clear of these items, you can effectively regulate your caloric intake and adopt healthier eating habits that support eating 1400 calories a day female, promoting a reduction in body mass. Furthermore, initiatives like New York City’s Added Sugars Warning Rule signify a growing awareness of dietary impacts, aiming to equip consumers with better information regarding health risks associated with high added sugars intake, set to be enforced starting October 4, 2025. It is also important to note the limitations of the data presented, including the reliance on single 24-hour dietary recalls and the cross-sectional nature of the NHANES data, which may affect the conclusions drawn about sugary beverage consumption.
Is the 1400-Calorie Diet Effective and Safe for Women?
For many women seeking to reduce their size, eating 1400 calories a day female can be a practical choice, especially when paired with regular physical activity. A year-long study conducted with a large sample size reinforces the effectiveness of this approach. However, it is crucial to prioritize nutrient-dense foods to fulfill essential vitamin and mineral requirements, thereby minimizing the risk of nutritional deficiencies.
Monitoring your body’s reactions to this caloric limit is key; adjustments may be necessary based on individual health responses. As mentioned by registered dietitian Jillian Kubala, it’s important to select healthy, sustainable methods for reducing body mass over more extreme dietary patterns. This corresponds with findings from the case study titled 'Sustainable Methods for Reducing Body Mass,' which highlights the effectiveness of healthier, less extreme strategies for achieving a healthier physique.
Consulting with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian is highly advisable to ensure that the diet aligns with your specific health needs. If symptoms such as fatigue or dizziness arise, it may indicate the need to reevaluate your caloric intake and overall dietary approach. Additionally, body composition should be assessed using bioelectrical impedance analysis, and various health metrics should be collected through blood tests and questionnaires to ensure comprehensive monitoring of health while eating 1400 calories a day female.
Adopting a sustainable method not only supports weight loss but also safeguards long-term health.
Conclusion
The 1400-calorie diet presents a structured and effective approach for women looking to manage their weight while ensuring they receive essential nutrients. By establishing a clear caloric framework, this diet enables individuals to engage in mindful eating and portion control, which are vital for sustainable weight loss. It emphasizes the importance of balancing caloric intake with energy expenditure, allowing for personalized adjustments based on factors like age, activity level, and metabolic rate.
Meal planning plays a key role in successfully adhering to this diet, promoting the incorporation of a variety of food groups, including:
- Lean proteins
- Whole grains
- Fruits
- Vegetables
These elements not only enhance satiety but also provide essential vitamins and minerals necessary for overall health. Avoiding high-calorie, low-nutrient foods, such as:
- Sugary beverages
- Processed snacks
further supports weight management goals by reducing unnecessary caloric intake.
While the 1400-calorie diet can be effective, it is crucial to approach it with a focus on health and personalization. Consulting with healthcare professionals ensures that individual dietary needs are met and helps prevent potential nutritional deficiencies. By prioritizing nutrient-dense foods and maintaining regular physical activity, individuals can achieve their weight loss objectives while fostering long-term health and well-being. This balanced strategy underscores the significance of sustainable weight loss methods over extreme dietary patterns, ultimately leading to a healthier lifestyle.




