Overview
The article focuses on the various types of belly fat in females, emphasizing the distinction between visceral and subcutaneous fat, and their associated health risks. This is supported by statistical evidence on obesity prevalence among women and the importance of understanding these fat types to inform effective management strategies, including diet, exercise, and mental health support.
Introduction
In a world increasingly aware of health and wellness, belly fat has emerged as a critical concern, particularly for women navigating the complexities of aging. This article delves into the nuances of abdominal fat, distinguishing between its harmful visceral and less concerning subcutaneous forms, while highlighting the alarming statistics surrounding obesity rates among women.
With insights from health experts and recent research, it explores the multifaceted factors contributing to belly fat and its associated health risks, including cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
Furthermore, the discussion extends to effective strategies for managing belly fat through diet, exercise, and mental well-being, emphasizing the importance of holistic approaches.
By understanding these elements, women can empower themselves to take charge of their health and enhance their overall quality of life.
Understanding Belly Fat: An Overview for Women
Belly fat, or abdominal fat, poses a significant issue for many women, especially as they navigate the aging process, which can be illustrated through various types of belly fat female pictures. It is essential to understand that not all abdominal fat is the same; distinguishing between subcutaneous and visceral fat, as illustrated in various types of belly fat female pictures, is vital for evaluating risks. In recent findings, 24.9% of Mexican American girls are classified as obese, underscoring the prevalence of this issue.
Furthermore, a report highlights that the body mass index (BMI), often used to define obesity, has limitations, as it does not directly measure body fat or its distribution. This limitation is especially significant when considering the consequences depicted in types of belly fat female pictures. Ruth Petersen, MD, director of the CDC's Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity, observes:
- Numerous factors contribute to obesity such as:
- genes
- specific medications
- inadequate sleep
- gut microbiome
- stress
- availability of affordable food
- safe areas for activity
- access to medical care
Understanding these factors helps us identify potential prevention and treatment strategies.
Research by Eekelen et al. (2019) examines the adherence to dietary guidelines in relation to visceral fat and liver fat in middle-aged individuals, emphasizing the connection between diet and fat distribution.
Additionally, the prevalence of severe obesity has been reported at 9.4%, with rates peaking at 12.0% in adults aged 40-59. Significantly, this data indicates that severe obesity impacts females more notably, with a prevalence of 12.1% compared to 6.7% in men, especially in the 40-59 age group. This is additionally backed by the case study titled 'Prevalence of Severe Obesity in Adults,' which emphasizes the increasing worry of obesity and its effects on female well-being.
These statistics highlight the critical link between physical fitness, stress levels, and types of belly fat female pictures. By addressing these elements, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of how to effectively manage their wellness and enhance their overall well-being.
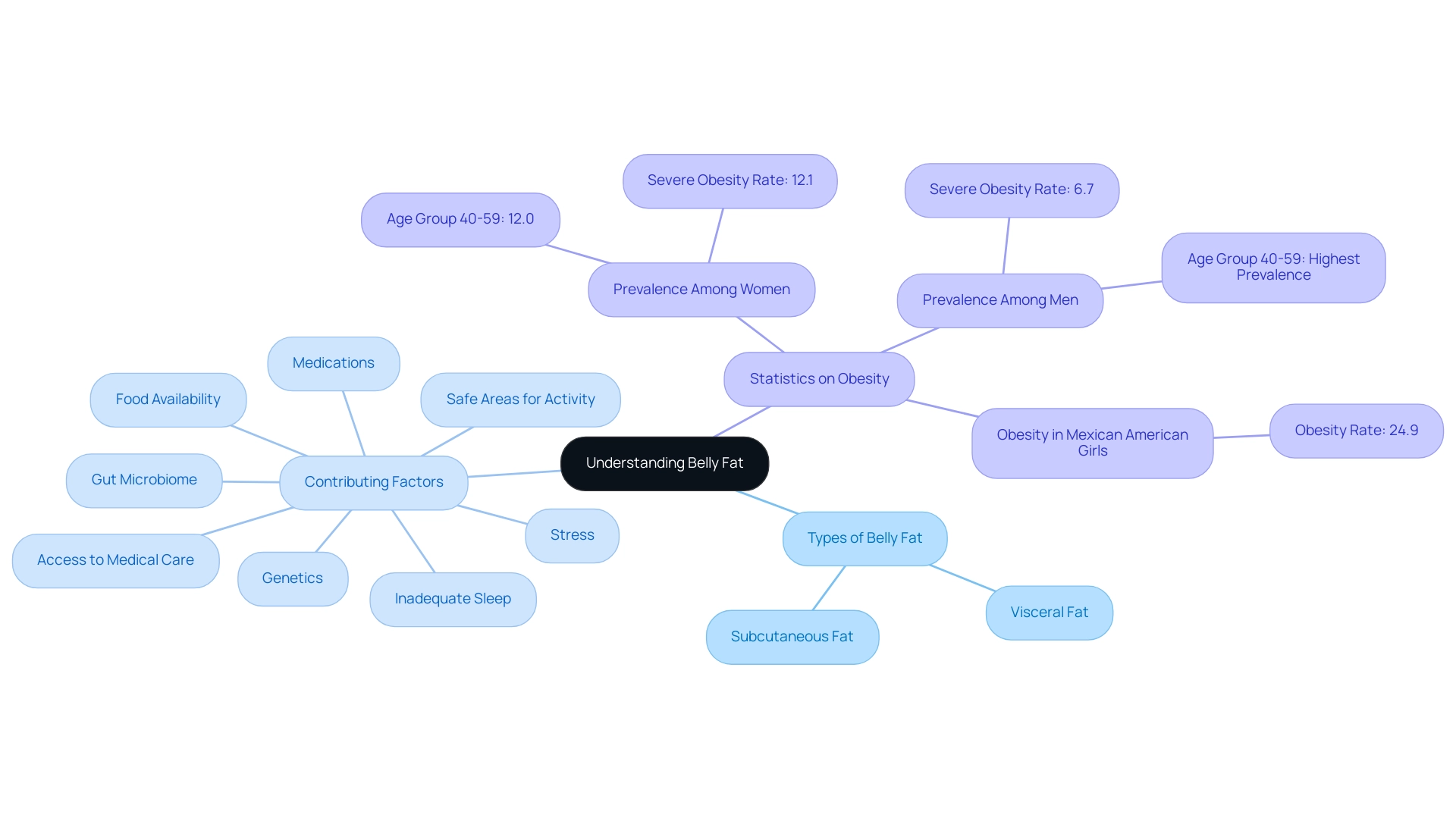
The Different Types of Belly Fat: Visceral vs. Subcutaneous
There are different types of belly fat, which can be broadly classified into two categories: visceral fat and subcutaneous fat, as illustrated in types of belly fat female pictures. Visceral fat, which lies deep within the abdominal cavity and surrounds essential organs, is linked to considerable risks, including heart disease and diabetes. Among the types of belly fat female pictures, this type is particularly concerning for women, as studies highlight that a healthy waist-height ratio should not exceed 0.5.
In contrast, subcutaneous fat lies just beneath the skin and is generally considered less harmful. Understanding these distinctions is critical, as excessive visceral fat can adversely affect overall health and performance in professional settings. The Cleveland Clinic emphasizes the importance of addressing concerns regarding visceral fat, stating,
If you suspect you may have too much visceral fat in your belly, talk to your healthcare provider.
However, it is important to note that the research on eating speed and its relationship to visceral fat has limitations, such as the reliance on self-reported eating speed and a smaller sample size of females compared to males. This highlights the need for further research, as discussed in the case study titled "Limitations and Future Directions in Eating Speed Research," which calls for standardized protocols to better assess eating speed and its effects on abdominal fat mass. Given the growing evidence linking visceral fat to medical complications, particularly in women, it becomes imperative to monitor body composition and consult professionals for tailored advice regarding types of belly fat female pictures.
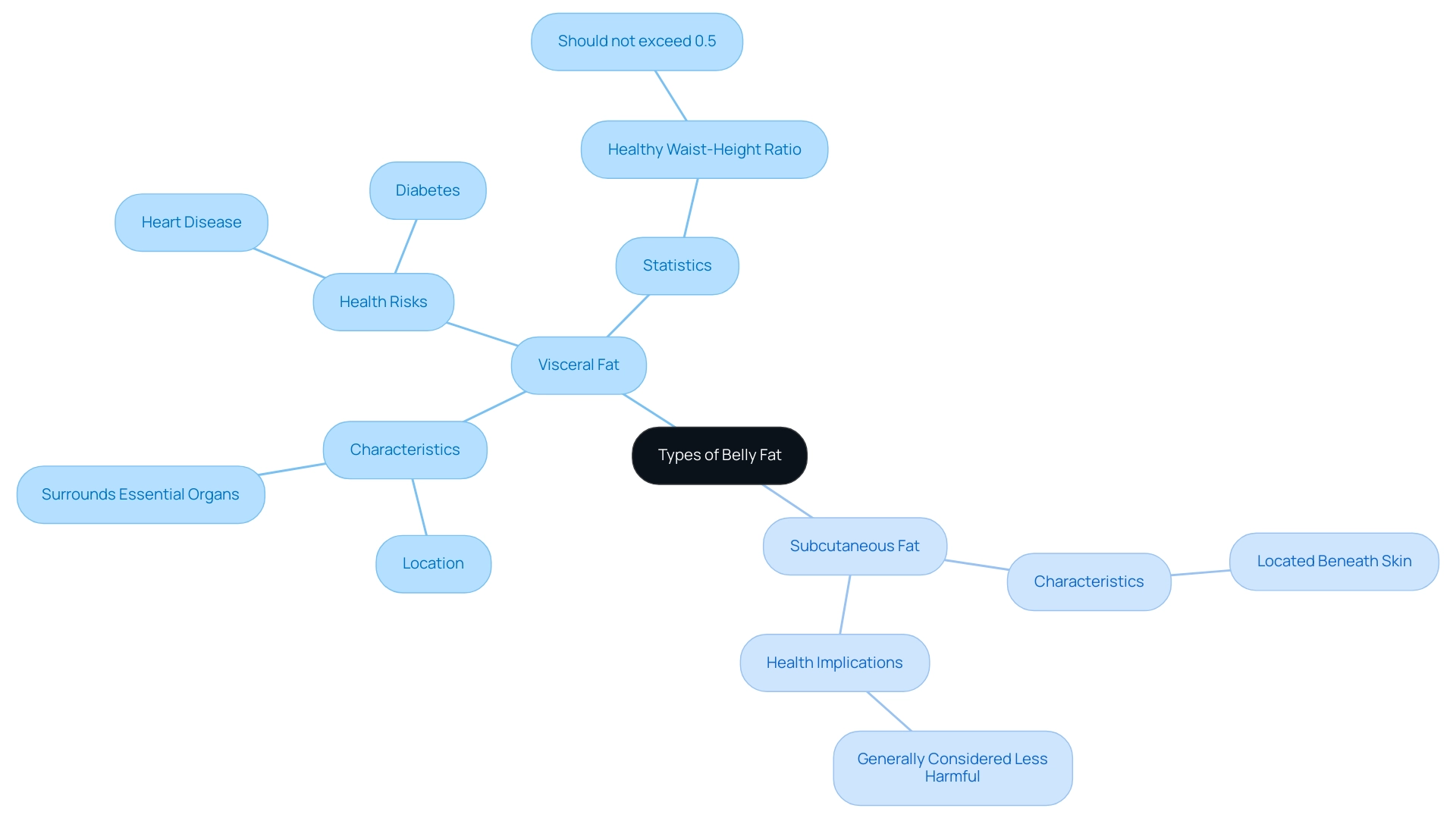
Health Risks Associated with Excess Belly Fat
Excess belly fat, especially visceral fat, presents considerable risks, including a higher chance of developing cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. The World Health Organization underscores these concerns by defining obesity as a BMI of 30 or greater, with one in eight individuals currently living with obesity. This alarming statistic emphasizes the urgency of understanding the consequences of excess abdominal fat.
It's important to note that BMI should be used alongside measurements of abdominal fat to assess risk accurately. Moreover, visceral fat can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to mood swings and decreased energy levels, which may adversely affect workplace performance. As noted by Dr. Chika Anekwe,
As a nation, we must confront these challenges and find systemwide solutions for reducing socioeconomic barriers and eliminating racism, in order to improve individual agency and ability to lead healthier lives.
The case study titled 'Takeaways on Visceral Fat' highlights the significance of comprehending visceral fat and its associated risks, advocating a holistic approach to well-being that incorporates diet, exercise, sleep, and stress reduction. It is essential for females to acknowledge these risks and adopt proactive strategies to address these health challenges efficiently, particularly considering the most recent health risks linked to types of belly fat female pictures in 2024.
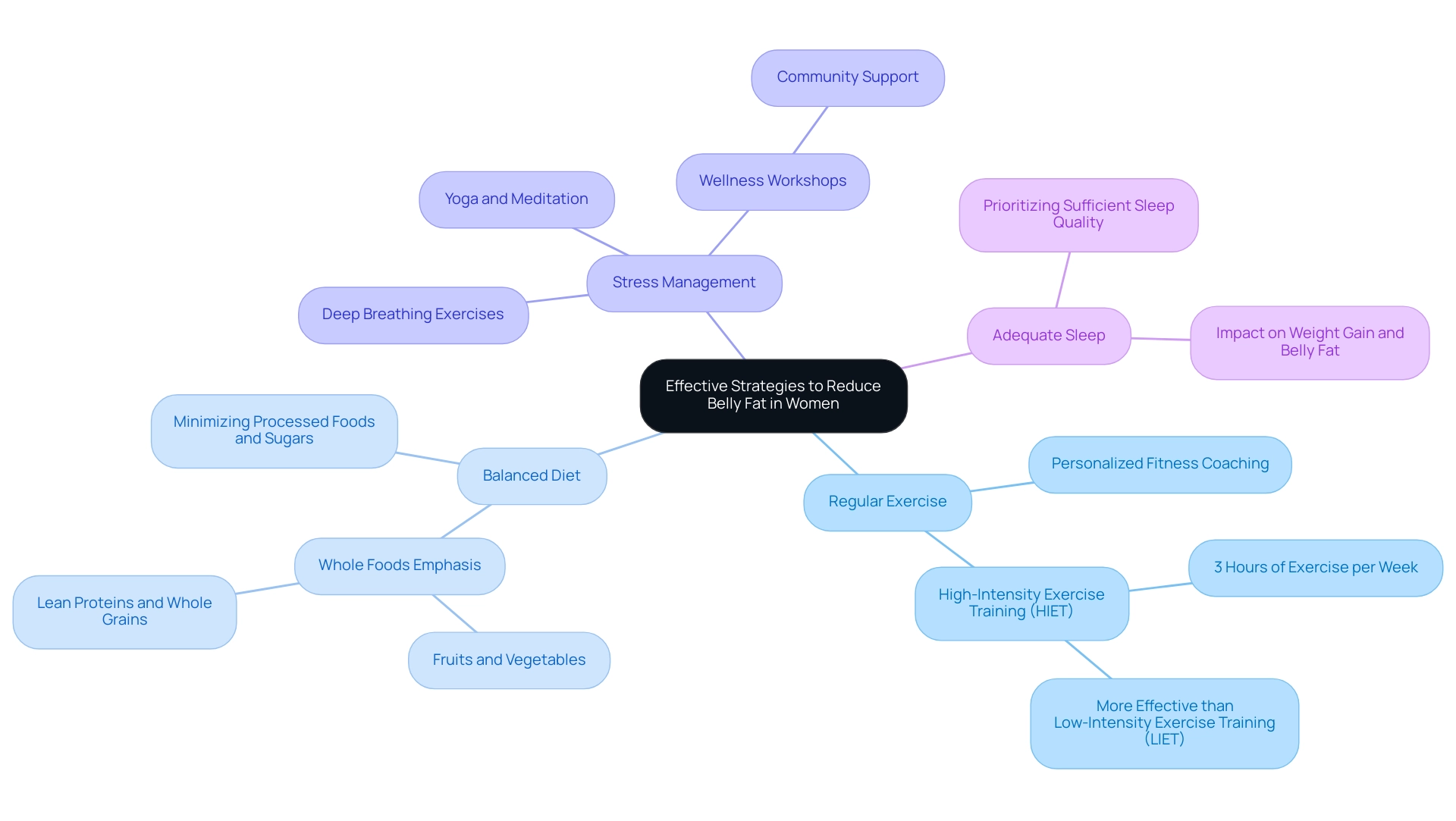
Effective Strategies to Reduce Belly Fat in Women
To effectively reduce abdominal fat, individuals can adopt several evidence-based strategies, supported by Foresight Health Coaching’s comprehensive programs:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in both aerobic and strength training exercises is critical for burning calories and building muscle, essential components for fat loss. Foresight offers personalized fitness coaching tailored to individual needs, ensuring structured workouts that are particularly beneficial for obese women with metabolic syndrome. A study revealed that participants in a high-intensity exercise training (HIET) program, which involved approximately 3 hours of exercise per week, achieved significant body composition improvements compared to those in a low-intensity exercise training (LIET) program.
- Balanced Diet: Emphasizing whole foods—fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains—while minimizing processed foods and sugars can greatly influence abdominal fat reduction. Foresight's nutritional guidance supports this approach, helping clients make informed dietary choices. As noted by health experts, even a modest exercise program aligned with recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and the American College of Sports Medicine can prevent significant increases in visceral abdominal fat. This underscores the dietary impact on fat management and the effectiveness of small commitments to exercise.
- Stress Management: Engaging in stress-relieving activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can reduce cortisol levels, a hormone associated with fat accumulation, thus assisting in fat reduction around the abdomen. Foresight incorporates wellness workshops focused on stress management techniques, fostering a community of support among participants. These workshops are included in corporate memberships, allowing employees to engage in group learning and mutual support.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritizing sufficient sleep is essential, as poor sleep quality is associated with weight gain and increased belly fat. By implementing these strategies, women can work towards achieving a healthier body composition and enhanced overall well-being, supported by evidence that even sedentary, unfit women can successfully adhere to supervised exercise programs offered through Foresight's app-based delivery. For HR Benefits Managers, exploring Foresight's corporate membership options can offer customized wellness solutions for employees, enhancing workplace well-being and productivity. Contact us to learn more about how our programs can benefit your organization.
The Role of Diet and Exercise in Belly Fat Management
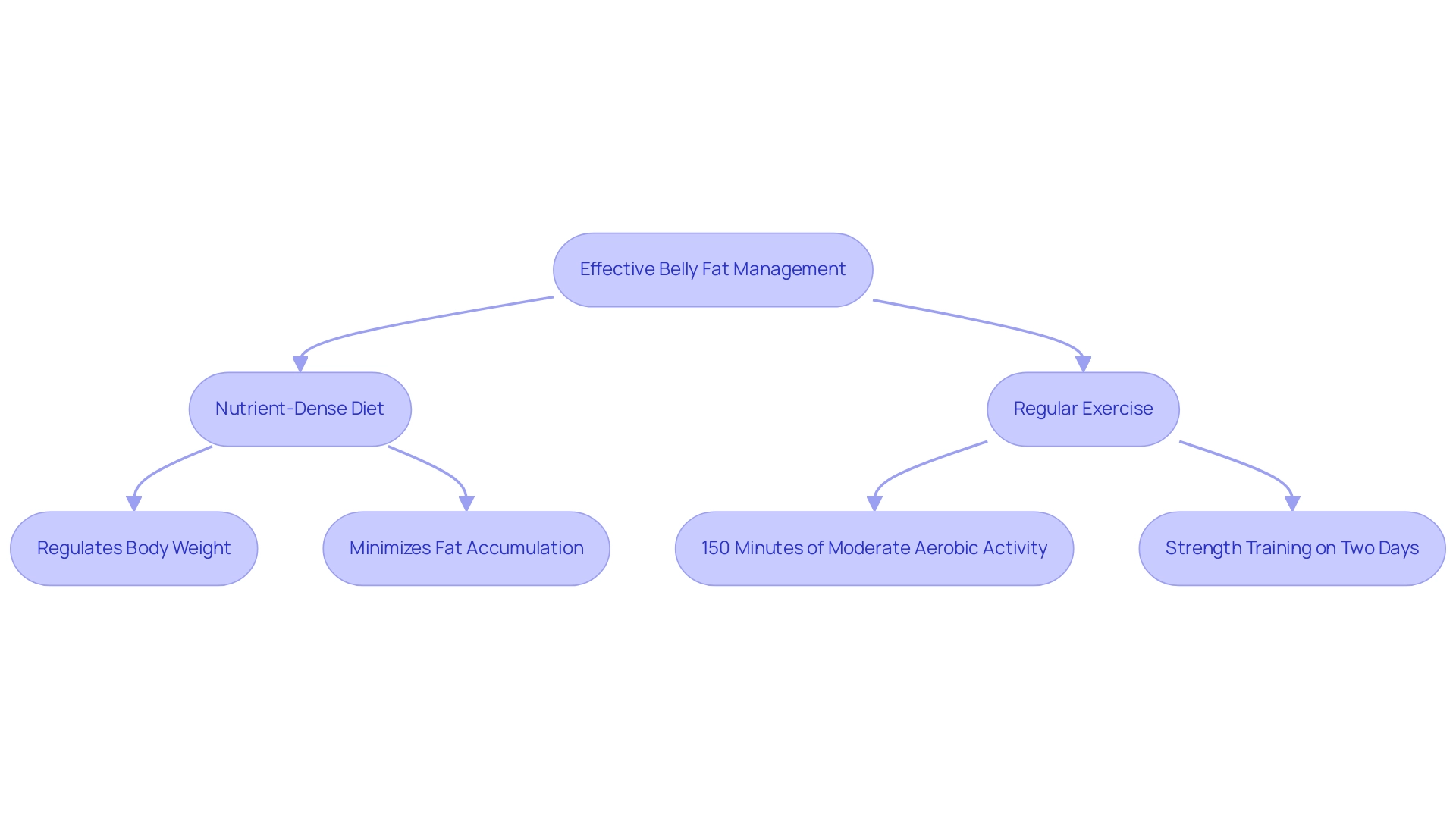
Effective management of belly fat hinges on a strategic combination of diet and exercise. A nutrient-dense diet is essential for regulating body weight and minimizing fat accumulation. Consistent physical activity not only aids in burning calories but also significantly improves metabolic function.
In 2024, it is recommended that women engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly, alongside strength training exercises on two or more days. This balanced regimen not only aids in the decrease of abdominal fat but also promotes better overall well-being and improved workplace performance. Notably, studies indicate that all groups showed similar decreases in abdominal visceral fat of approximately 25%, underscoring the effectiveness of these strategies.
As the BMJ Publishing Group states, 'BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content,' emphasizing the importance of relying on credible sources when considering diet and exercise plans. Additionally, case studies, such as the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test, provide insights into how metabolic health is influenced by dietary choices and physical activity, reinforcing that a well-rounded approach is vital for effective fat management.
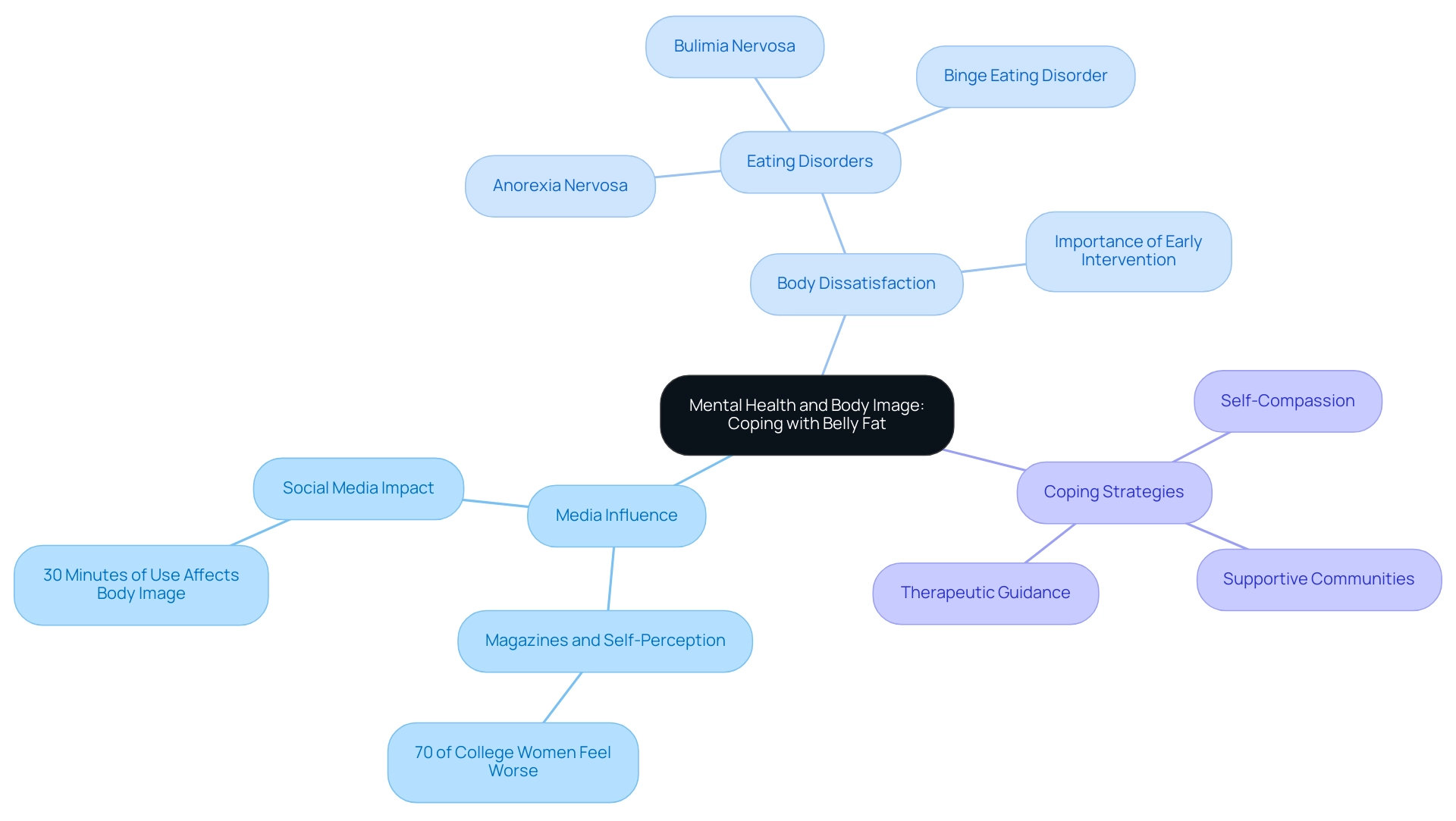
Mental Health and Body Image: Coping with Belly Fat
Dealing with belly fat presents significant emotional challenges for many individuals, often resulting in detrimental effects on body image and self-esteem. Research indicates that a staggering 70% of female college students report feeling worse about their appearance after engaging with magazines, highlighting the pervasive influence of media on self-perception. As noted by Fardouly, one study found that using social media for as little as 30 minutes a day can negatively change the way young individuals view their own bodies, further exacerbating body image issues.
To combat these negative feelings, fostering a positive body image and embracing self-compassion are essential. Engaging in supportive communities, whether through social media platforms or local groups, can provide the necessary encouragement and motivation. Furthermore, seeking guidance from a therapist or counselor can be instrumental in navigating complex emotions tied to body image.
Body dissatisfaction is a well-known contributor to the development and maintenance of eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa, emphasizing the importance of early intervention for body image concerns. Additionally, the prevalence of disordered eating in Fiji, which doubled from 13% to 29%, underscores the urgent need to address these issues. By prioritizing mental health and promoting a culture of confidence and well-being, individuals not only enhance their self-esteem but also improve their overall health, allowing them to focus on other important aspects of life.
Recode Performance offers services designed to help individuals take the worry out of staying healthy, enabling them to feel proud and confident walking through life. This holistic approach not only benefits individual individuals but also enhances performance in both personal and professional arenas, making it a crucial consideration for HR Benefits Managers looking to foster a supportive work environment.
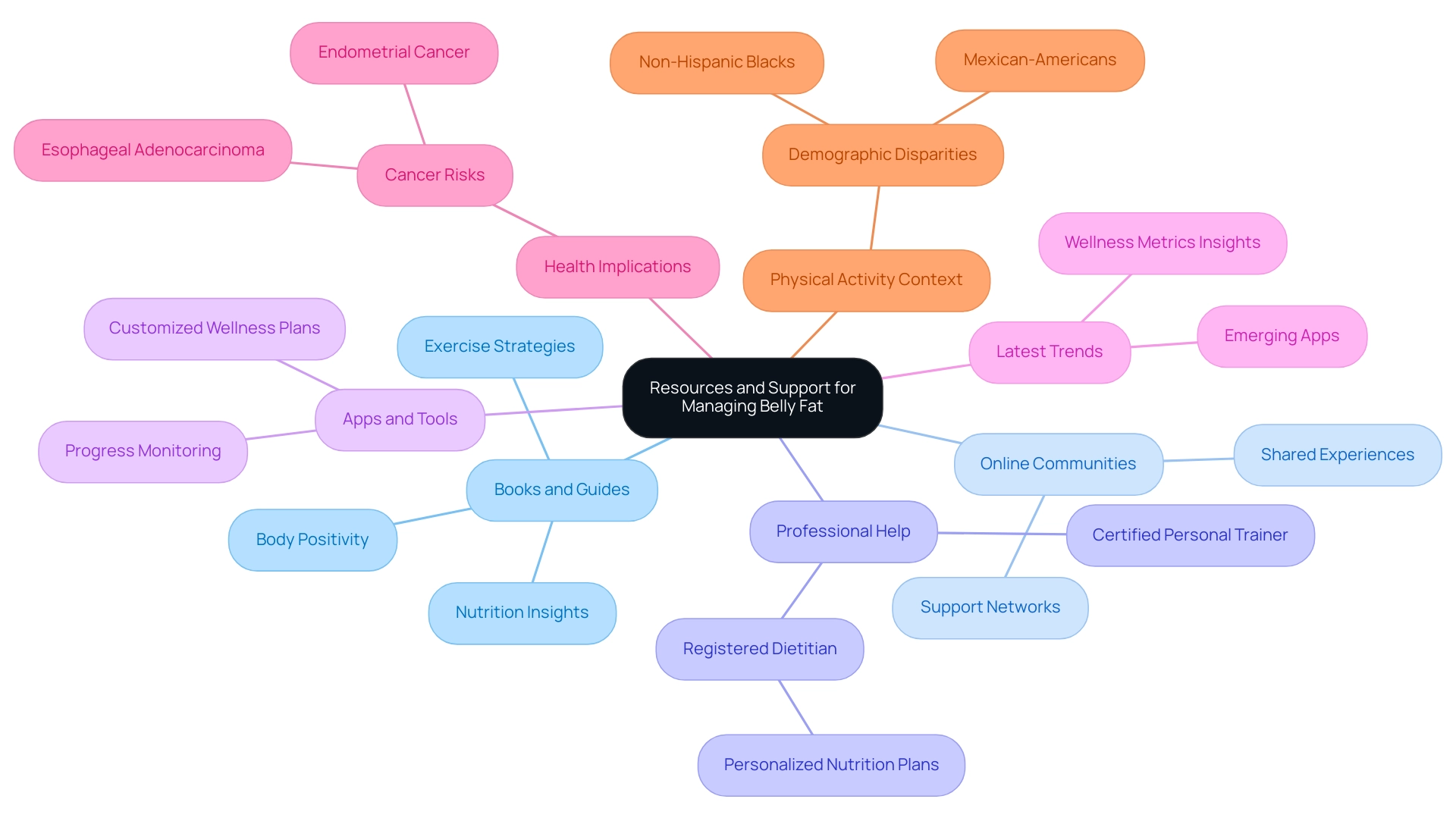
Resources and Support for Managing Belly Fat
For women aiming to effectively manage belly fat, a variety of streamlined resources can significantly aid their journey:
- Books and Guides: Reading materials focusing on nutrition, exercise, and body positivity can provide valuable insights and strategies. Health coaches emphasize the importance of fostering a positive mindset while pursuing fitness goals. Given that obesity negatively impacts reproduction and fertility, understanding these resources is crucial.
- Online Communities: Engaging with forums or social media groups can create a supportive network, offering motivation and shared experiences among those facing similar challenges. Expert opinions emphasize how community support can improve commitment to wellness objectives.
- Professional Help: Consulting with a registered dietitian or certified personal trainer offers tailored guidance, crucial for addressing individual needs. Evidence indicates that professional assistance results in greater success rates in managing belly fat, with dietitians offering personalized nutrition plans that address specific concerns. This aligns with the statistic that the prevalence of severe obesity increased from 7.7% to 9.7% from 2013 to 2023, emphasizing the need for effective management strategies.
- Apps and Tools: Utilizing fitness applications, such as our interactive iPhone/Android app, enables users to monitor their progress and uphold accountability. This app is designed to consolidate relevant wellness and fitness information and programming, simplifying personalized wellness and fitness planning. By utilizing proven methods, the app curates customized plans that lessen management stress, thus proving advantageous for many individuals in their wellness management efforts.
- Latest Trends: In 2024, the landscape of resources available for managing abdominal fat continues to evolve, with new apps and tools emerging that are specifically designed for women. These advancements not only aid in monitoring types of belly fat female pictures but also provide insights into overall wellness metrics.
- Health Implications: Research indicates that individuals with obesity are at a higher risk for developing various cancers, including endometrial and esophageal adenocarcinoma. This underscores the serious consequences of obesity and the importance of utilizing available resources.
- Physical Activity Context: Notably, higher proportions of inactivity have been reported among non-Hispanic blacks and Mexican-Americans compared to non-Hispanic whites, highlighting the need for targeted interventions in these demographics.
By utilizing these diverse resources, women can enhance their path toward improved health and well-being, equipped with the knowledge and support necessary for success. As Samuel D. Emmerich states, "Monitoring obesity prevalence is important for understanding trends over time," reinforcing the relevance of these resources.
Conclusion
Understanding belly fat and its implications for health is crucial for women, especially as they age. The distinction between visceral and subcutaneous fat highlights the varying health risks associated with these types of abdominal fat. With alarming statistics indicating a significant prevalence of obesity among women, it becomes evident that addressing belly fat is not just about aesthetics but also about safeguarding overall health.
Effective strategies for managing belly fat include:
- A combination of regular exercise
- A balanced diet
- Stress management
- Adequate sleep
Each of these elements plays a vital role in reducing visceral fat and promoting a healthier body composition. Furthermore, fostering a positive mental outlook and body image is essential, as the emotional challenges tied to belly fat can impact self-esteem and overall well-being.
Utilizing available resources, such as books, online communities, and professional guidance, can empower women on their journey to better health. By approaching belly fat management holistically, women can enhance their quality of life and mitigate health risks associated with excess abdominal fat. The journey towards health is multifaceted, but with the right knowledge and support, it is achievable.